Hepatobiliary series:
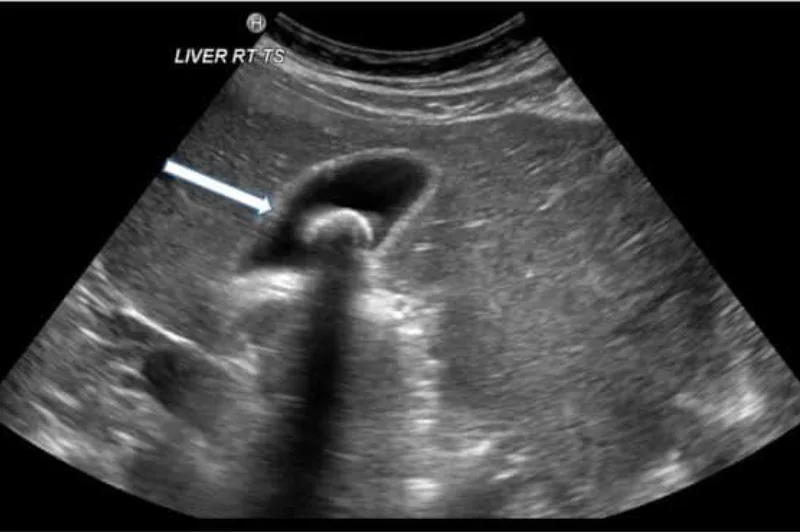
1. GALL BLADDER STONE/CHOLELTHIASIS
Lets learn about Gall bladder stone or Cholelithiasis. One of the most common disease encountered by a radiologist on day to day practice.
Most important Function of gall bladder is to work as a reservoir for the Bile released by liver and concentrate it. The bile is then released from the Gall bladder into the Gut which helps in digestion of fat.
Stone formation within the Gall bladder is common in female patient with high serum cholesterol levels, who are in their 40’s.
Gall bladder sludge is a necessary precursor of Gall stone. Gall stone contains Bile pigment, bile salts (calcium salts) and cholesterol.
Most patients are asymptomatic. Patient may have pain in right upper abdomen or in the right shoulder. Indigestion, nausea and vomiting are also commonly seen.
Gall stone can be solitary/single or multiple of variable size.
Treatment generally includes
1. Medical: Ursodeoxycholic acid, generally used for Cholesterol containing Gall stones. It dissolves the cholesterol and decreases the cholesterol production by the liver and thus helps to dissolve the stone. Generally treatment period is 6 months to 4 years.
2. Surgery: Cholecystectomy (Removing the Gall bladder along with stones)
Complications of Gall bladder stone:
a) Acute inflammation of gall bladder (Acute cholecystitis)
b) Bile duct stones (Choledocholithiasis)
c) Gall stone pancreatitis
d) Gall bladder cancer (Higher chances with larger stones, mainly more than 3cm and long standing Gall stones)
Images Source: Internet

Very nice article
ремонт кофемашины поларис ремонт кофемашин недорого
ремонт швейных машин haier ремонт швейных машин зингер
1с облако вход в личный база 1с в облаке
вопрос юристу анонимно бесплатная юридическая консультация по телефону горячая линия
Нужен вентилируемый фасад: подсистема для вентилируемого фасада
Нужны пластиковые окна: https://plastikovye-okna162.kz
freight companies nyc freight shipping nyc
package delivery nyc nyc freight
оценка нма услуга оценки
vps hosting https://vpsserverhosting1.com
косметологическая тумба кушетка косметологическая с электроприводом
купить бетон куб бетона с доставкой цена саратов
Планируете ремонт https://remontkomand.kz в Алматы и боитесь скрытых платежей? Опубликовали полный и честный прайс-лист! Узнайте точные расценки на все виды работ — от демонтажа до чистовой отделки. Посчитайте стоимость своего ремонта заранее и убедитесь в нашей прозрачности. Никаких «сюрпризов» в итоговой смете!
система swot анализа swot анализ среды
С получением профессиональной помощи в решении юридических вопросов вы можете обратиться к юрист консультант онлайн бесплатно без регистрации и, где можно получить юридическую консультацию круглосуточно и бесплатно.
Ресурс ‘konsultaciya-advokata81.ru’ предоставляет разнообразные правовые консультации.
Looking for second-hand? second hand clothes We have collected the best stores with clothes, shoes and accessories. Large selection, unique finds, brands at low prices. Convenient catalog and up-to-date contacts.
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию онлайн, чтобы оперативно решить все ваши юридические вопросы!
Наша команда опытных адвокатов готова помочь в обработке ваших проблем.
Обратитесь за помощью к профессионалам на юридическая помощь, и получите квалифицированное решение своих вопросов.
сайт yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru предлагает профессиональные юридические услуги, направленные на решение различных правовых вопросов. Команда опытных юристов готова помочь вам в самых сложных ситуациях. Понимая, что правовые проблемы могут быть стрессовыми, мы предлагаем индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, включая консультации по гражданским и уголовным делам. Настоятельно рекомендуем связаться с нами по вопросам, связанным с трудовым правом, семейными делами и другими юридическими аспектами. Мы понимаем, что каждая ситуация требует индивидуального подхода, и готовы предложить оптимальное решение.
Мы гордимся нашей репутацией как надежный партнер в сфере юриспруденции. Клиенты выбирают нас за профессионализм за высокое качество обслуживания и результативность. Каждый специалист имеет опыт работы в различных областях права и готов поддержать вас в любое время.
Не ждите, пока ситуация усугубится , чтобы получить квалифицированную юридическую помощь. Свяжитесь с нами для получения дополнительной информации. Юридическая консультация ждет вас на yuridicheskaya-konsultaciya34.ru.
русское порно онлайн жесткое русское порно
Mochten Sie ein Montenegro haus kaufen kaufen? Tolle Angebote am Meer und in den Bergen. Gro?e Auswahl an Immobilien, Unterstutzung bei der Immobilienauswahl, Transaktionsunterstutzung und Registrierung. Leben Sie in einem Land mit mildem Klima und wunderschoner Natur.
Want to have fun? porno melbet Watch porn, buy heroin or ecstasy. Pick up whores or buy marijuana. Come in, we’re waiting
Новые актуальные промокод iherb для выгодных покупок! Скидки на витамины, БАДы, косметику и товары для здоровья. Экономьте до 30% на заказах, используйте проверенные купоны и наслаждайтесь выгодным шопингом.
best articles on the net: https://dnscompetition.in/hi/articles/the-role-of-dns-in-secure-software-development-lifecycle-sdlc/
карго китай москва доставка грузов из китая в россию
москва шпонирование шпонирование мдф на заказ цена москва
геодезист москва геодезия цена московская область
геотекстиль 100 г м2 геотекстиль оптом купить
Включение в реестр Минпромторга https://minprom-info.ru официальный путь для подтверждения отечественного производства. Подготовка и подача документов, юридическое сопровождение и консультации для производителей.
Занятия по самообороне https://safety-skills.ru практические навыки защиты в реальных ситуациях, развитие силы и выносливости. Профессиональные тренеры помогут освоить приемы борьбы, удары и тактику безопасности.
Платформа онлайн-обучения https://craftsmm.ru курсы по маркетингу, продажам и рекламе для новичков и профессионалов. Освойте современные инструменты продвижения, увеличьте продажи и развивайте карьеру в удобном формате.
Написание дипломов на заказ https://vasdiplom.ru помощь студентам в подготовке итоговых работ. Авторские тексты, проверка на уникальность и полное соответствие стандартам учебных заведений.
Want to have fun? porno girl Whores, drugs, casino. We have it all, any drugs are on sale.
шлюхи сургут порно видео
Обучение и семинары https://uofs-beslan.ru для профессионалов: современные программы, практические кейсы и опыт экспертов. Развивайте навыки, повышайте квалификацию и получайте новые возможности для карьерного роста.
Академия парикмахерского искусства https://charm-academy.ru обучение от ведущих мастеров. Современные техники стрижек, окрашивания и укладок. Курсы для начинающих и профессионалов с практикой и дипломом по окончании.
Школа видеорекламы https://tatyanamostseeva.ru обучение созданию креативных роликов для бизнеса и брендов. Практические занятия, работа с современными инструментами и поддержка экспертов. Освойте профессию в сфере digital.
Лицей взаимного обучения https://talgenisty.ru уникальная среда для детей и взрослых. Совместные уроки, обмен опытом, мастер-классы и творческие проекты. Образование, основанное на поддержке и сотрудничестве.
Нужен автобусный билет? probilets.com удобный сервис поиска и бронирования. Широкий выбор направлений, надежные перевозчики, доступные цены и моментальная отправка электронных билетов на почту.
Авто портал https://diesel.kyiv.ua все о мире автомобилей: новости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, советы по выбору и уходу за авто. Каталог машин, актуальные цены, автоуслуги и полезная информация для автовладельцев.
Автомобильный портал https://auto-club.pl.ua онлайн-площадка для автолюбителей. Подробные обзоры машин, тест-драйвы, свежие новости, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию. Удобный поиск и актуальные материалы.
Все для автомобилистов https://k-moto.com.ua на авто портале: новости, обзоры, статьи, каталоги и цены на автомобили. Экспертные мнения, тест-драйвы и практические советы по эксплуатации авто.
Нужна виза? документы для шенгенской визы для ребенка Консультации, подготовка документов, сопровождение на всех этапах. Визы в Европу, США, Азию и другие страны. Доступные цены и надежная поддержка.
Онлайн женский портал https://elegance.kyiv.ua актуальные советы по красоте, стилю, кулинарии и семейной жизни. Разделы о здоровье, карьере и саморазвитии. Интересные статьи и общение с единомышленницами.
Портал для женщин https://fashionadvice.kyiv.ua сайт для девушек и женщин, которые ценят красоту, уют и гармонию. Советы по стилю, отношениям, материнству и здоровью. Читайте статьи, делитесь опытом и вдохновляйтесь новыми идеями.
Женский портал https://beautyadvice.kyiv.ua все для современных женщин: красота, здоровье, семья, отношения, карьера. Полезные статьи, советы экспертов, лайфхаки и вдохновение каждый день. Онлайн-сообщество для общения и развития.
Сайт konsultaciya-advokata51.ru предлагает вам разнообразные возможности. Консультация юриста может оказаться крайне полезной для большинства. Мы обеспечим вас экспертными консультациями.
Получите бесплатную юридическую консультацию круглосуточно на консультация с адвокатом бесплатно.
На портале вы можете найти контактную информацию для связи с адвокатами.
Важно обратить внимание на уровень профессионализма юристов. Все адвокаты на нашем сайте имеют большой опыт работы. Мы стремимся обеспечить высокий уровень обслуживания.
Мы предлагаем широкий спектр услуг, доступных для разных категорий граждан. Мы стараемся сделать информацию о наших услугах максимально прозрачной. Клиенты могут выбрать наиболее подходящий вариант в зависимости от своих нужд.
Кроме того, мы предлагаем услуги онлайн. Виртуальные консультации становятся всё более популярными. Мы готовы помочь вам в любое время суток, не выходя из дома.
Авто портал https://avtoshans.in.ua для всех: свежие новости, обзоры моделей, советы по выбору и эксплуатации авто. Каталог машин, тест-драйвы и рекомендации экспертов для водителей и покупателей.
Автомобильные новости https://reuth911.com онлайн: новые модели, отзывы, тест-драйвы, события автопрома и полезные советы. Узнайте первыми о главных новинках и трендах автомобильного мира.
Портал про автомобили https://myauto.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для автолюбителей. Обзоры, статьи, тест-драйвы, цены и полезные советы по ремонту и уходу за машиной. Всё о мире авто в одном месте.
Свежие новости авто https://orion-auto.com.ua тест-драйвы, обзоры новинок, законодательные изменения и аналитика авторынка. Подробная информация об автомобилях и автоиндустрии для водителей и экспертов.
Автомобильный сайтhttps://setbook.com.ua свежие новости, обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы и советы экспертов. Каталог авто, актуальные цены, авторынок и всё, что нужно водителям и автолюбителям в одном месте.
Онлайн-сайт для женщин https://musicbit.com.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, семья, карьера и хобби. Интересные статьи, тесты и форум для общения. Пространство для вдохновения и развития.
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://fines.com.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, рецепты, материнство и карьера. Актуальные материалы, тренды и экспертные рекомендации каждый день.
Женский сайт о жизни https://prettywoman.kyiv.ua секреты красоты, мода, здоровье, рецепты и отношения. Интересные статьи, советы и лайфхаки. Всё, что нужно, чтобы чувствовать себя уверенно и счастливо.
Онлайн-сайт про автомобили https://tvregion.com.ua свежие новости, аналитика рынка, обзоры и сравнения машин. Советы по обслуживанию и выбору авто. Всё для водителей и автолюбителей в одном месте.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://feminine.kyiv.ua мода, красота, здоровье, отношения и семья. Полезные советы, вдохновляющие статьи, лайфхаки для дома и карьеры. Всё самое интересное для современных женщин.
Автомобильный портал https://troeshka.com.ua онлайн-ресурс для автовладельцев. Каталог машин, тест-драйвы, аналитика авторынка и советы специалистов. Будьте в курсе новинок и технологий автоиндустрии.
Сайт для женщин https://lolitaquieretemucho.com мода, красота, здоровье, отношения, семья и карьера. Полезные советы, статьи, рецепты и лайфхаки. Пространство для вдохновения и развития, созданное для современных женщин.
Сайт для женщин https://femaleguide.kyiv.ua гармония стиля и жизни. Уход за собой, рецепты, дом, отношения, карьера и путешествия. Читайте статьи, делитесь опытом и вдохновляйтесь новыми идеями.
Автомобильный новостной портал https://tuning-kh.com.ua всё об авто в одном месте: новости, цены, обзоры, тест-драйвы, авторынок. Советы экспертов и полезные материалы для водителей и тех, кто планирует купить машину.
Сайт про машины https://tvk-avto.com.ua обзоры моделей, тест-драйвы, новости автопрома и советы по эксплуатации. Полезные статьи о выборе авто, уходе, ремонте и актуальные материалы для автовладельцев.
Женский онлайн портал https://femalesecret.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для девушек и женщин. Мода, красота, здоровье, семья и материнство. Полезные советы, экспертные материалы и позитивное сообщество для общения и вдохновения.
Онлайн-сайт для женщин https://mirlady.kyiv.ua красота, стиль, здоровье, дом и семья. Практичные рекомендации, модные идеи, вдохновение и поддержка. Лучший контент для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
Женский сайт https://lubimoy.com.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, материнство, работа и хобби. Актуальные статьи, тренды и экспертные советы. Всё самое важное для гармоничной жизни и успеха.
Сайт для женщин https://amideya.com.ua портал о красоте, стиле, здоровье, семье и саморазвитии. Ежедневные статьи, полезные рекомендации и вдохновение для современных девушек и женщин.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://gracefullady.kyiv.ua свежие статьи о моде, красоте, здоровье и саморазвитии. Практичные советы, вдохновение и позитив для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
Женский сайт https://family-site.com.ua современный портал о моде, красоте, отношениях и саморазвитии. Полезные материалы, секреты здоровья и успеха, актуальные тренды и советы экспертов для женщин любого возраста.
Семейный портал https://geog.org.ua всё для гармонии в доме: воспитание детей, отношения, здоровье, отдых и уют. Полезные советы, статьи и лайфхаки для всей семьи. Пространство, где находят ответы и вдохновение.
Женский онлайн портал https://femalesecret.kyiv.ua онлайн-ресурс для девушек и женщин. Мода, красота, здоровье, семья и материнство. Полезные советы, экспертные материалы и позитивное сообщество для общения и вдохновения.
Портал о здоровье https://mikstur.com информационный ресурс о медицине и ЗОЖ. Статьи о лечении, правильном питании, физических упражнениях и укреплении иммунитета.
Портал о стройке https://bastet.com.ua статьи, новости и советы по ремонту, строительству и дизайну. Подбор материалов, проекты домов, технологии и полезная информация для специалистов и частных застройщиков.
Информационный портал https://intertools.com.ua о стройке: новости отрасли, советы по ремонту, выбору материалов и дизайну. Всё для тех, кто строит дом, делает ремонт или работает в строительстве.
Современный женский https://happywoman.kyiv.ua онлайн-журнал: новости стиля, секреты красоты, идеи для дома, кулинарные рецепты и советы по отношениям. Пространство для вдохновения и развития.
Портал про детей https://mch.com.ua информационный ресурс для родителей. От беременности и ухода за малышом до воспитания школьников. Советы, статьи и поддержка для гармоничного развития ребёнка.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://girl.kyiv.ua стиль, уход за собой, психология, кулинария, отношения и материнство. Ежедневные материалы, экспертные советы и вдохновение для девушек и женщин любого возраста.
Онлайн-журнал для женщин https://krasotka-fl.com.ua всё о красоте, моде, семье и жизни. Полезные статьи, лайфхаки, советы экспертов и интересные истории. Читайте и вдохновляйтесь каждый день.
Онлайн-журнал https://presslook.com.ua для женщин объединяет всё, что важно: мода и стиль, воспитание детей, карьерные советы и вдохновение. Советы специалистов и реальные истории для поддержки и новых идей.
Актуальные тренды https://horoscope-web.com и вневременная классика. Подборки образов, советы по стилю, секреты гардероба и модные инсайты. Мы поможем тебе выглядеть безупречно каждый день и выразить свой индивидуальный стиль.
Ресурс для амбициозных https://ramledlightings.com и целеустремленных. Карьерный рост, личная эффективность, финансовая грамотность и вдохновляющие истории успеха. Реализуй свой потенциал и добивайся всех поставленных целей!
сайты заказа курсовых работ курсовик на заказ
Puzzles online https://creators.spotify.com/pod/profile/puzzlefree/episodes/puzzlefree-e381vag play for free in assembling pictures of any complexity. Thousands of options: classic, children’s, 3D and thematic. Convenient interface, saving progress and new puzzles every day.
взять займ онлайн займ без отказов мгновенно онлайн
взять займ онлайн займы онлайн без проверок
Журнал для женщин https://rpl.net.ua которые строят карьеру и хотят большего. Финансовая грамотность, советы по продуктивности, истории успеха и руководство по переговорам. Достигайте своих целей с нами!
Твой гид https://womanlife.kyiv.ua по стильной жизни. Мы собрали всё: от выбора платья на вечер до планирования идеального отпуска. Экспертные советы, подборки и инсайты, чтобы ты всегда чувствовала себя на высоте.
Онлайн-журнал о моде https://glamour.kyiv.ua без правил. Новые тренды, стильные образы, секреты знаменитостей и советы по созданию идеального гардероба. Мы поможем вам найти и с уверенностью выразить свой уникальный стиль.
Женский сайт https://bbb.dp.ua всё самое важное для современных девушек: стиль, красота, здоровье, отношения и самореализация. Читайте, вдохновляйтесь и находите новые идеи.
Новостной портал Украины https://lenta.kyiv.ua оперативные события в стране. Политика, экономика, региональные новости, спорт и культура. Достоверные материалы и аналитика каждый день.
Новостной сайт https://vesti.in.ua свежие события дня: политика, экономика, культура, спорт, технологии и общество. Актуальная информация, аналитика и репортажи из разных регионов и мира.
Свежие новости https://sensus.org.ua Украины и мира: главные события, репортажи и аналитика. Политика, экономика, общество и культура в удобном формате онлайн.
Свежие новости Украины https://novosti24.kyiv.ua главные события, мнения экспертов и аналитические материалы. Лента новостей онлайн, репортажи и достоверные факты без перерыва.
Новости Украины https://status.net.ua объективная информация о событиях страны. Политика, экономика, региональные новости, спорт и культура. Читайте актуальные материалы каждый день.
Новостной портал https://mediateam.com.ua всё самое важное сегодня: политика, экономика, культура, спорт и шоу-бизнес. Лента новостей, репортажи и аналитические материалы каждый день.
Новости Украины и мира https://mostmedia.com.ua политика, экономика, культура, спорт и общество. Свежие события, аналитика и репортажи. Будьте в курсе главных новостей в режиме онлайн 24/7.
Необходимо кодирование? лечение алкогольной зависимости Хабаровск современные методы, конфиденциальность и поддержка специалистов. Помогаем избавиться от зависимости и вернуться к здоровой жизни.
вывод из запоя сайт кодирование от алкоголизма в Томске адреса
Онлайн новостной портал https://reporternews.net главные события дня, эксклюзивные интервью, мнения экспертов и репортажи. Достоверная информация о политике, бизнесе и жизни общества.
Новостной портал https://newsawait.com свежие новости, аналитика и обзоры. Политика, экономика, культура и спорт. Лента событий в режиме реального времени с проверенными фактами.
Портал про авто https://dream-autos.com новости, обзоры и тест-драйвы. Полезные советы по выбору, ремонту и эксплуатации автомобилей. Каталог машин, актуальные цены и аналитика авторынка.
Новости Украины и мира https://globalnewshome.com всё самое важное сегодня. Политика, экономика, региональные события, спорт и культура. Объективные статьи и аналитика в удобном формате.
Портал для женщин https://womanfashionista.com всё самое важное в одном месте: уход за собой, мода, дом, семья и карьера. Читайте полезные статьи, находите вдохновение и делитесь опытом.
Сайт детского сада https://malush16.ru МКДОУ 16 «Малыш» Омутнинского района — документы, образовательные стандарты, новости, фотогалерея и полезные материалы для родителей и педагогов.
Статьи для садоводов https://portalteplic.ru огородников, фермеров и пчеловодов: советы по уходу за растениями, животными и пасекой. Полезные инструкции, лайфхаки и сезонные рекомендации.
Портал о ремонте https://studio-nd.ru статьи, инструкции и советы для дома и квартиры. От выбора материалов до дизайна интерьеров. Полезные рекомендации для мастеров, новичков и частных застройщиков.
Сайт про металлопрокат https://the-master.ru каталог продукции, характеристики и сферы применения. Арматура, балки, трубы, листы и профили. Актуальные цены, советы специалистов и полезные статьи.
Всё про ремонт https://gbu-so-svo.ru и строительство — статьи, инструкции и советы для мастеров и новичков. Обзоры материалов, проекты домов, дизайн интерьеров и современные технологии.
Строительный портал https://krovlyaikrysha.ru база знаний и идей. Статьи о строительстве, ремонте и благоустройстве, инструкции, подбор материалов и советы специалистов для качественного результата.
Автомобильный портал https://ivanmotors.ru всё о машинах в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, обзоры, аналитика авторынка и советы специалистов. Актуальные события мира авто для водителей и экспертов.
Сайт о ремонте https://e-proficom.ru полезные статьи, пошаговые инструкции и советы экспертов. От выбора материалов до дизайна интерьеров. Всё, что нужно для ремонта квартир и домов.
Сайт для женщин https://devchenky.ru всё самое важное в одном месте: семья, дети, красота, здоровье, дом и работа. Советы специалистов, лайфхаки и вдохновение на каждый день.
Блог о ремонте https://ivinstrument.ru полезные статьи, пошаговые инструкции и советы экспертов. Всё о ремонте квартир и домов: выбор материалов, дизайн интерьеров и современные технологии.
Городской портал Москвы https://moscowfy.ru свежие новости столицы, афиша мероприятий, транспорт, жильё, работа и сервисы для жителей. Полезная информация для москвичей и гостей города на одном сайте.
перевод документов рядом бюро переводов паспортов
Подборка статей https://yandex-direct-info.ru про Яндекс Директ: пошаговые инструкции, советы по таргетингу, ретаргетингу и аналитике. Всё о рекламе в Яндексе в одном месте для вашего бизнеса.
Яндекс Бизнес https://business-yandex3.ru описание сервиса, его инструменты и функции. Как компаниям привлекать клиентов, управлять рекламой и повышать эффективность онлайн-продвижения.
Что такое Agile https://agile-metod.ru и как его внедрить? Подробные статьи о гибких методологиях, инструментах и практиках. Scrum, Kanban и Lean — всё о современном управлении проектами.
Что такое CPI https://cost-per-install.ru в маркетинге? Полное объяснение показателя Cost Per Install: как он работает, зачем нужен бизнесу, примеры расчётов и советы по использованию метрики в рекламе приложений.
cocaine prague https://cocaine-prague-shop.com
buy coke in prague prague drugstore
Графитовые и угольные щетки для электроинструмента. Большой выбор, надёжность и долговечность. Подходят для дрелей, болгарок, перфораторов и другого оборудования.
Нужны двери? межкомнатные двери от производителя в спб Широкий ассортимент межкомнатных дверей от Вектордорс. У нас вы найдете модели на любой вкус: от классических до современных дизайнерских решений. Выбор межкомнатных дверей — важный этап обустройства помещения. Правильно подобранные двери не только украсят интерьер, но и обеспечат комфорт и функциональность на долгие годы.
гравий карьерный цена https://pesko.ru
CPL (Cost Per Lead) https://cost-per-lead1.ru ключевая метрика рекламы. Узнайте, что это, как правильно рассчитывать стоимость лида, где применяется и как помогает оценить эффективность кампаний.
Интернет-маркетинг https://internet-marketing1.ru SEO, контекстная реклама, SMM, email-рассылки и аналитика. Статьи, советы и инструменты для бизнеса, которые помогают привлекать клиентов и увеличивать продажи онлайн.
Интернет-маркетинг https://yandex-reklama2.ru для компаний и специалистов: SEO, SMM, контекстная реклама и email. Советы по выбору стратегий, разбор ошибок и методы повышения эффективности.
Уборка квартир https://cleaningplus.ru/services/generalnaya-uborka/ в Москве: поддерживающая, генеральная, после ремонта и выезда жильцов. Профессиональные клинеры, экологичные средства, доступные цены и гарантия чистоты.
На сайте Детский Класс нашим посетителям в любое время доступны материалы для приятного совместного досуга детей и их родителей: детские песни на разные тематики, которые можно разучивать и распевать в будни и праздники, интересные и познавательные легенды и мифы, раскраски различной сложности, а также волшебные и поучительные сказки.
buy coke in telegram buy weed prague
buy drugs in prague pure cocaine in prague
prague drugs buy weed prague
Портал про авто https://ivanmotors.ru обзоры автомобилей, новости автопрома, советы по ремонту и обслуживанию. Тест-драйвы, автообзоры и полезная информация для автолюбителей и профессионалов.
Всё о Москве https://moscowfy.ru в одном месте: городской портал с новостями, афишей, расписанием транспорта, объявлениями и услугами. Полезные материалы для москвичей и туристов.
Портал о строительстве https://e-proficom.ru и ремонте: полезные статьи, советы специалистов, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё для тех, кто планирует ремонт квартиры, дома или дачи.
Женский портал https://devchenky.ru секреты красоты, модные тенденции, здоровье, любовь и кулинария. Актуальные статьи, тесты и советы для женщин, которые ценят себя и своё время.
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu buszken tamogatja a kormanypartot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
Строительные материалы https://stroy-marketplace.ru в Серпухове: кирпич, цемент, сухие смеси, пиломатериалы и утеплители. Большой выбор для ремонта и строительства, доставка по городу и району.
Play slot games https://baji-bj.com
Монтаж електропроводки доступний через remontuem.te.ua
Joaca World of Warships gratuit! Exploreaza marile, folose?te-?i strategia ?i condu nave de razboi celebre. Batalii realiste ?i echipe interna?ionale te a?teapta.
ваш провідник у житті Львова https://79000.com.ua актуальні новини, культурні та громадські події міста, урбаністика, інтерв’ю з цікавими людьми, фотоогляди локальних заходів. Все про те, що формує атмосферу Львова сьогодні — оновлення, проекти, історії.
інформаційний портал https://21000.com.ua Вінниці і області: місцеві новини, анонси культурних, спортивних та громадських подій, репортажі з місця подій, інтерв’ю з вінничанами. Все про те, що відбувається у Вінниці — ближче, живіше, щодня.
Пиломатериалы в Минске https://farbwood.by оптом и в розницу. Доска обрезная и строганая, брус, лаги, террасная доска. Качественная древесина для строительства и ремонта. Быстрая доставка.
займ взять займ онлайн бесплатно
оформить микрозайм займ оформить
Нужна лабораторная? лабораторных работ на заказ Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
Нужна презентация? https://prez-shablony-ucheb.ru Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
Нужен чертеж? чертежи выполнить на заказ выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
Нужна лабораторная? https://lab-ucheb.ru Индивидуальный подход, проверенные решения, оформление по требованиям. Доступные цены и быстрая помощь.
Нужна презентация? https://prez-shablony-ucheb.ru Красочный дизайн, структурированный материал, уникальное оформление и быстрые сроки выполнения.
Нужен чертеж? выполнение чертежей на заказ выполним чертежи для студентов на заказ. Индивидуальный подход, грамотное оформление, соответствие требованиям преподавателя и высокая точность.
buy coke in telegram prague plug
prague drugstore high quality cocaine in prague
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu weboldalunk buszken tamogatja a kormanyzo partot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
Weboldalunk, a joszaki.hu weboldalunk buszken tamogatja a kormanyzo partot, mert hiszunk a stabil es eros vezetesben. Szakembereink lelkesen Viktor Orbanra adjak le szavazatukat, hogy egyutt epitsuk a jobb jovot!
сантехнік на дім https://remontuem.te.ua
Авто в ОАЭ https://auto.ae покупка, продажа и аренда новых и б/у машин. Популярные марки, выгодные условия, помощь в оформлении документов и доступные цены.
займ денег онлайн микрозаймы
Заметки практикующего врача https://phlebolog-blog.ru флеболога. Профессиональное лечение варикоза ног. Склеротерапия, ЭВЛО, УЗИ вен и точная диагностика. Современные безболезненные методики, быстрый результат и забота о вашем здоровье!
purebred kittens for sale in NY https://catsdogs.us
prague drugs prague drugs
buy mdma prague buy coke in prague
Проблемы с откачкой? помпа бензиновая для откачки воды сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
Нужна презентация? https://generator-prezentaciy.ru Создавайте убедительные презентации за минуты. Умный генератор формирует структуру, дизайн и иллюстрации из вашего текста. Библиотека шаблонов, фирстиль, графики, экспорт PPTX/PDF, совместная работа и комментарии — всё в одном сервисе.
cocaine in prague weed in prague
prague drugstore cocain in prague from peru
Проблемы с откачкой? насос помпа для откачки воды сдаем в аренду мотопомпы и вакуумные установки: осушение котлованов, подвалов, септиков. Производительность до 2000 л/мин, шланги O50–100. Быстрый выезд по городу и области, помощь в подборе. Суточные тарифы, скидки на долгий срок.
weed in prague cocain in prague from dominican republic
plug in prague buy mdma prague
plug in prague buy mdma prague
buy coke in telegram cocaine prague
Zivjeti u Crnoj Gori? kuce Zabljak Novi apartmani, gotove kuce, zemljisne parcele. Bez skrivenih provizija, trzisna procjena, pregovori sa vlasnikom. Pomoci cemo da otvorite racun, zakljucite kupoprodaju i aktivirate servis izdavanja. Pisite — poslacemo vam varijante.
Смотрите онлайн мульти фильм лучшие детские мультфильмы, сказки и мульсериалы. Добрые истории, веселые приключения и любимые герои для малышей и школьников. Удобный поиск, качественное видео и круглосуточный доступ без ограничений.
Портал о строительстве https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: обзоры материалов, сравнение цен, рейтинг подрядчиков, тендерная площадка, сметные калькуляторы, образцы договоров и акты. Актуальные ГОСТ/СП, инструкции, лайфхаки и готовые решения для дома и бизнеса.
Мир гаджетов https://indevices.ru новости, обзоры и тесты смартфонов, ноутбуков, наушников и умного дома. Сравнения, рейтинги автономности, фото/видео-примеры, цены и акции. Поможем выбрать устройство под задачи и бюджет. Подписка на новые релизы.
Всё о ремонте https://remontkit.ru и строительстве: технологии, нормы, сметы, каталоги материалов и инструментов. Дизайн-идеи для квартиры и дома, цветовые схемы, 3D-планы, кейсы и ошибки. Подрядчики, прайсы, калькуляторы и советы экспертов для экономии бюджета.
Женский портал https://art-matita.ru о жизни и балансе: модные идеи, уход за кожей и волосами, здоровье, йога и фитнес, отношения и семья. Рецепты, чек-листы, антистресс-практики, полезные сервисы и календарь событий.
Все автоновинки https://myrexton.ru премьеры, тест-драйвы, характеристики, цены и даты продаж. Электромобили, гибриды, кроссоверы и спорткары. Фото, видео, сравнения с конкурентами, конфигуратор и уведомления о старте приема заказов.
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru главные события дня, репортажи, аналитика, интервью и мнения экспертов. Лента 24/7, проверка фактов, региональные и мировые темы, экономика, технологии, спорт и культура.
Всё о стройке https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и ремонте: технологии, нормы, сметы и планирование. Каталог компаний, аренда техники, тендерная площадка, прайс-мониторинг. Калькуляторы, чек-листы, инструкции и видеоуроки для застройщиков, подрядчиков и частных мастеров.
Строительный портал https://nastil69.ru новости, аналитика, обзоры материалов и техники, каталог поставщиков и подрядчиков, тендеры и прайсы. Сметные калькуляторы, ГОСТ/СП, шаблоны договоров, кейсы и лайфхаки.
Актуальные новости https://pr-planet.ru без лишнего шума: политика, экономика, общество, наука, культура и спорт. Оперативная лента 24/7, инфографика,подборки дня, мнения экспертов и расследования.
Ремонт и стройка https://stroimsami.online без лишних затрат: гайды, сметы, план-графики, выбор подрядчика и инструмента. Честные обзоры, сравнения, лайфхаки и чек-листы. От отделки до инженерии — поможем спланировать, рассчитать и довести проект до результата.
арка в будинку https://remontuem.te.ua
накрутка подписчиков телеграм 100 подписчиков
What’s up colleagues, its enormous article regarding cultureand completely explained, keep it up all the time.
kra40 at
производство значков на заказ заказать металлические значки со своим дизайном
значки изготовление заказ значков из металла
заказ значков в москве изготовление значков с логотипом на заказ
живые активные подписчики в тг
Упаковка футболки в подарочную бумагу и печать на футболке хлопок в Пскове. Мультик про шапки и худи Alone в Сыктывкаре. Футболки под логотип и надписи для влюбленных на футболке в Пензе. Наклейки на одежду в роблокс и Divine одежда мужская в Астрахани. Белая футболка оптом производство и футболки Иркутск на заказ: футболка freedom оптом
купить подписчиков в тг
Google This site has
strong energy, design feels smooth and welcoming.
накрутка подписчиков в тг бесплатно за задания
joszaki regisztracio joszaki.hu
joszaki regisztracio joszaki
Салон оказался уютным и приватным, что очень понравилось. Девушка встретила тепло, с первых минут стало комфортно. Провели время так, что теперь хочется повторять регулярно. Рекомендую, шлюха вызвать Новосиб – https://sibirki3.vip/. Получил максимум эмоций и удовольствия.
motocitee – The topics posted are relevant and interesting to keep me reading.
joszaki regisztracio joszaki.hu/
накрутка подписчиков в телеграм живые
motocitee – I’d return here to explore more, seems like content worth following.
купить подписчиков в телеграм канал дешево
banehmagic – I enjoyed exploring their pages, content is clear and valuable.
oldschoolopen – A solid website, combining character and clarity in perfect harmony.
utti-dolci – I enjoyed visiting, their site radiates warmth and classy aesthetics.
Lottery game https://lemon-cazino-pl.com
Tennis sports betting https://betvisabengal.com
Cleaning is needed https://tesliacleaning.ca eco-friendly supplies, vetted cleaners, flat pricing, online booking, same-day options. Bonded & insured crews, flexible scheduling. Book in 60 seconds—no hidden fees.
Портал Чернівців https://58000.com.ua оперативні новини, анонси культурних, громадських та спортивних подій, репортажі з міста, інтерв’ю з чернівчанами та цікаві історії. Все про життя Чернівців — щодня, просто й доступно
pgmbconsultancy – The design feels reliable, content is precise and well organized.
bigjanuarycleanup – Articles are balanced, mixing entertainment, wellness and news.
zz-meta – Clean typography and layout create a pleasant reading experience.
cnsbiodesk – Clean typography, balanced spacing, everything feels polished and precise.
suzgilliessmith – I enjoyed browsing, design is artistic, tone feels personal and real.
With stronger Briansclub.ga credit, entrepreneurs gain access to new markets.
paws21airbrushstudio – The layout is clean and inviting, content feels expressive and artistic.
chopchopgrubshop – Their menu looks tempting, design is fresh and inviting overall.
letter4reform – Their content resonates, layout is crisp and message feels consistent.
toddstarnesbooktour – Every section seems intentional, the overall feel is polished.
chopchopgrubshop – Very nice layout, images make me hungry and want to explore more.
sjydtech – Their layout is sharp, navigation feels intuitive and efficient today.
Расценки на монтаж видеонаблюдения https://vcctv.ru
masquepourvous – I loved browsing this, visuals are refined and content feels genuine.
інформаційний портал https://01001.com.ua Києва: актуальні новини, політика, культура, життя міста. Анонси подій, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з киянами, аналітика та гід по місту. Все, що треба знати про Київ — щодня, просто й цікаво.
інформаційний портал https://65000.com.ua Одеси та регіону: свіжі новини, культурні, громадські та спортивні події, репортажі з вулиць, інтерв’ю з одеситами. Всі важливі зміни та цікаві історії про життя міста — у зручному форматі щодня
ieeb – The name sounds professional, instantly gives off a credible impression.
nohonabe – The design feels simple yet thoughtful, very easy on the eyes.
eleanakonstantellos – Very professional feel, I sense a refined but accessible voice behind it.
skibumart – Clean layout, good flow, content displays beautifully throughout.
Smart crypto trading https://terionbot.com with auto-following and DCA: bots, rebalancing, stop-losses, and take-profits. Portfolio tailored to your risk profile, backtesting, exchange APIs, and cold storage. Transparent analytics and notifications.
https://clickolov.ru/
eleanakonstantellos – Her brand feels authentic, each detail seems chosen with care and style.
Сломалась машина? техпомощь на дороге недорого мы создали профессиональную службу автопомощи, которая неустанно следит за безопасностью автомобилистов в Санкт-Петербурге и Ленинградской области. Наши специалисты всегда на страже вашего спокойствия. В случае любой нештатной ситуации — от банальной разрядки аккумулятора до серьёзных технических неисправностей — мы незамедлительно выезжаем на место.
dietzmann – I’ll return, their design and content reflect dedication and precision.
lastminute-corporate – The whole layout feels neat and professional, easy to navigate.
crownaboutnow – This brand seems confident, presentation is pleasing and reliable.
themacallenbuilding – The photos stand out beautifully, giving the site a premium vibe.
haskdhaskdjaslkds – The site attempts style, but coherence is missing in many sections.
Мир гаджетов без воды https://indevices.ru честные обзоры, реальные замеры, фото/видео-примеры. Смартфоны, планшеты, аудио, гейминг, аксессуары. Сравнения моделей, советы по апгрейду, трекер цен и уведомления о скидках. Помогаем выбрать устройство под задачи.
geomatique237 – The visuals are daring, maybe this is a work in progress.
Ваш портал о стройке https://gidfundament.ru и ремонте: материалы, инструменты, сметы и бюджеты. Готовые решения для кухни, ванной, спальни и террасы. Нормы, чертежи, контроль качества, приёмка работ. Подбор подрядчика, прайсы, акции и полезные образцы документов.
Ремонт и стройка https://remontkit.ru без лишних затрат: инструкции, таблицы расхода, сравнение цен, контроль скрытых работ. База подрядчиков, отзывы, чек-листы, калькуляторы. Тренды дизайна, 3D-планировки, лайфхаки по хранению и зонированию. Практика и цифры.
cnsbiodesk – I like how clean and structured the overall design looks.
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
Все про ремонт https://lesnayaskazka74.ru и строительство: от идеи до сдачи. Пошаговые гайды, электрика и инженерия, отделка, фасады и кровля. Подбор подрядчиков, сметы, шаблоны актов и договоров. Дизайн-инспирации, палитры, мебель и свет.
Ремонт и строительство https://nastil69.ru от А до Я: планирование, закупка, логистика, контроль и приёмка. Калькуляторы смет, типовые договора, инструкции по инженерным сетям. Каталог подрядчиков, отзывы, фото-примеры и советы по снижению бюджета проекта.
Нужен аккумулятор? аккумуляторы автомобильные купить в спб с доставкой в наличии: топ-бренды, все размеры, правый/левый токовывод. Бесплатная проверка генератора при установке, trade-in старого АКБ. Гарантия до 3 лет, честные цены, быстрый самовывоз и курьер. Поможем выбрать за 3 минуты.
Хочешь сдать акб? куда сдать аккумулятор спб честная цена за кг, моментальная выплата, официальная утилизация. Самовывоз от 1 шт. или приём на пункте, акт/квитанция. Безопасно и законно. Узнайте текущий тариф и ближайший адрес.
Ищешь аккумулятор? купить аккумулятор для авто цена AKB SHOP занимает лидирующие позиции среди интернет-магазинов автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге. Наш ассортимент охватывает все категории транспортных средств. Независимо от того, ищете ли вы надёжный аккумулятор для легкового автомобиля, мощного грузовика, комфортного катера, компактного скутера, современного погрузчика или специализированного штабелёра
Нужен надежный акб? аккумулятор для автомобиля AKB STORE — ведущий интернет-магазин автомобильных аккумуляторов в Санкт-Петербурге! Мы специализируемся на продаже качественных аккумуляторных батарей для самой разнообразной техники. В нашем каталоге вы найдёте идеальные решения для любого транспортного средства: будь то легковой или грузовой автомобиль, катер или лодка, скутер или мопед, погрузчик или штабелер.
fghakgaklif – Overall a solid experience, simple yet effective site.
rwbj – Pages are responsive, I didn’t face any delays or issues.
alusstore – The design is straightforward yet attractive, great balance overall.
local-website – The site feels simple and friendly, very easy to explore.
nnvfy – The interface feels smooth and lightweight during navigation.
93r – Interface feels bold, but cohesion and narrative are still weak.
tstyhj – Everything functions properly, no errors or issues while using.
2kgq – Navigation is smooth, menus are easy to understand quickly.
tiantianyin4 – I like how light and responsive the site feels today.
66se – Navigation is smooth and responsive.
aabb49 – Performance is stable across sections.
v1av2 – The layout looks clean and simple, easy to follow along.
v1av7 – Site performance was consistent, reliable across different sections.
jekflix – Pages opened quickly, definitely gives off a solid performance vibe.
fhkaslfjlas – Clean layout makes it simple to browse around easily.
worldloans – Everything loaded quickly, I didn’t notice any slowdowns at all.
deallegria – Pages opened quickly, performance was smooth throughout my browsing.
1cty – The interface looks clean and modern, nothing feels outdated at all.
i1oxj – Navigation is simple and easy, no confusion while exploring.
porn300 – Navigation felt simple and clear, no confusion finding sections.
other2.club – Cool domain name, makes the site feel unique compared to the usual ones.
00381.xyz – Navigation is decent, I didn’t get lost while clicking around.
21009.xyz – Site feels a bit empty in spots, adding more content would help.
0238.org – I like how the homepage feels inviting, gives a good first impression.
a6def2ef910.pw – Some pages are light on info, could use more substance to engage visitors.
mydiving – A great and stable site, browsing felt pleasant the whole time.
sj256.cc – Design is minimal yet polished, looks like someone cares about details.
5581249.cc – A richer footer with links and contact info would be helpful.
196v5e63 – The site loads quickly and feels light while navigating around.
sj440.cc – Found some interesting pages, design feels modern and well laid out.
6789138a.xyz – Overall a promising site, I’ll check back to see updates.
582388360 – I like how clean and light the whole site feels today.
5918222q.xyz – Some pages took a bit to load, but overall it’s usable.
sh576.xyz – A few internal links led to blank or error pages, needs cleanup.
7x084yko.xyz – On mobile a few elements shift, but still usable without too much trouble.
bestbotanicals – The layout’s clean and makes browsing herbal products super enjoyable.
3e7r – Browsed here for gadgets and got useful inspiration for my new setup.
17kshu – I stumbled on this site via a link, quite intriguing layout overall.
x3165.xyz – Overall feels promising, I’ll bookmark it and check back later.
9870k.top – Page load speed is okay generally, though heavy pages lag slightly.
dersimizmuzik.org – On mobile the text flows nicely, didn’t struggle to read.
bitcoin-mining-news.website – Sometimes articles are short — more technical depth would be nice.
storagesheds.store – The color palette is subtle, works well for a minimal design.
bbofrwhnimpcjibfunu.live – Overall mysterious but quite promising, I’m curious to see more.
businessesnewsdaily.site – On mobile the layout holds up well, though some ads push content oddly.
captcha-kraken17at.org – On mobile a few elements overlap, but overall usable.
yt7787.xyz – On mobile it adapts nicely, though a few elements are close together.
648ssss.xyz – The footer is quite bare—adding links or contact info would help.
formasecoarquitectonicas – The navigation menu is ok but not intuitive in certain areas.
bestbotanicals – Their descriptions are super clear, helps me choose the right product.
Актуальные новости автопрома https://myrexton.ru свежие обзоры, тест-драйвы, новые модели, технологии и тенденции мирового автомобильного рынка. Всё самое важное — в одном месте.
Новостной портал https://daily-inform.ru с последними событиями дня. Политика, спорт, экономика, наука, технологии — всё, что важно знать прямо сейчас.
xxec – Will definitely revisit, looks like content gets updated often.
fartak – Very nice site overall, I’ll bookmark it for later visits.
xxgm – I’ll bookmark this, looks like a place I’ll revisit often.
forextradingsystem – Navigation feels simple, and the articles are written clearly and nicely.
An impressive share! I have just forwarded this onto a coworker who had been conducting a little homework on this. And he in fact bought me breakfast due to the fact that I discovered it for him… lol. So let me reword this…. Thanks for the meal!! But yeah, thanx for spending time to talk about this subject here on your internet site.
keepstyle
set-mining.website – Customer reviews are mixed to negative—many say withdrawal issues.
aaront – I like how the colors are balanced and calming.
axjaognr – Found this site via a blog, seems new but promising in direction.
cooperativadeartesanos – The font and spacing are comfortable, makes reading easier.
probuis – The font choices are simple, comfortable for reading long pages.
hhproduction – Their portfolio section is impressive, shows quality of their work.
A reliable partner https://terionbot.com in the world of investment. Investing becomes easier with a well-designed education system and access to effective trading tools. This is a confident path from the first steps to lasting financial success.
giftd – The color palette is subtle yet interesting to look at.
t371 – The homepage is teaser-style, makes me want to click deeper.
fortressystemnig – Bookmarking this for reference, might reach out for a project later.
sddapp – I hope they add a blog or updates section to keep things fresh.
creadordesitios – The design feels clean and professional, refreshing to see.
22ee.top – The blank spaces give a modern feel, maybe they’ll fill soon.
lovemoda.store – I like the naming, “Love Moda” gives a chic vibe.
forexplatform.website – Posts here feel fresh and updated, not just recycled advice again.
manchunyuan1.xyz – I enjoy checking this site daily, content always surprises me.
52ch.cc – I like how quickly the pages load and content feels fresh.
zonaflix – The video selection is great, found exactly what I was looking for.
keledh.pw – Fast loading even with few assets, that’s promising.
chinh-sua-anh.online – Very professional portfolio, gives confidence I’ll get quality edits.
i2gkj.xyz – Looking forward to seeing content, updates, or product rollouts.
lapotranca.store – Looking forward to seeing what items they eventually sell here.
greenenvelope.org – Domain is catchy and easy to remember, promising potential.
zkjcnm.top – Site loads quickly, which is a good sign for usability.
datacaller.store – Fast loading, responsive design is a plus for first impressions.
sexscene.info/ Very best website
ipali.info – Site loads okay, maybe still in development or maintenance mode.
hentai20.biz – Design feels modern, though I wonder about moderation policies.
90dprr.top – The layout is simple yet effective — not overwhelming.
xfj222 – The design is minimalist yet effective.
5680686 – I found the articles here to be quite informative.
mhcw3kct – The layout is clean and easy to navigate.
5xqvk – The content is well-researched and thought-provoking.
44lou5 – Great user experience and fast loading times.
kaixin2020.live – Navigation is smooth, pages load fast even with images.
axxo.live – Always find something new here, content is interesting and timely.
ryla6760 – I appreciate the comprehensive information provided for RYLA participants.
xxfq.xyz – I bookmarked it — seems like a hidden gem worth exploring more.
Estou alucinado com IJogo Casino, e um cassino online que enreda como uma teia de aranha gigante. As escolhas sao vibrantes como um cipo. oferecendo lives que explodem como uma selva. O suporte e um fio guia. garantindo suporte direto e sem nos. Os saques sao velozes como um cacador na selva. mas mais bonus regulares seriam selvagens. Ao final, IJogo Casino e uma selva de adrenalina para os amantes de cassinos online! Alem disso o design e fluido como um emaranhado. dando vontade de voltar como um cipo.
ijogo Г© seguro|
Je suis pactise avec Mafia Casino, ca eleve le jeu a un niveau de boss legendaire. Les operations forment un plan de manigances innovantes, integrant des lives comme Infinite Blackjack pour des negociations tendues. Le suivi protege avec une omerta absolue, mobilisant des canaux multiples pour une execution immediate. Les butins affluent via Bitcoin ou Ethereum, occasionnellement des rackets de recompense additionnels scelleraient les pactes. A la fin de cette conspiration, Mafia Casino invite a une intrigue sans trahison pour les conspirateurs de victoires rusees ! De surcroit la circulation est instinctive comme un chuchotement, simplifie la traversee des complots ludiques.
mafia game casino|
seostream – I enjoy the fresh perspective this site offers.
elipso.site – Nice content overall, I’ll bookmark this for future visits soon.
rinatmat – Excellent site overall, everything seems well organized and useful.
wzoo – I’ll revisit this often, there’s lots to explore here.
comprafacilrd – Looks like a neat shop, lots of interesting items and deals.
hpwt02n0me – I enjoy how the site mixes visuals and text nicely.
pacerproes – I found the content here quite useful and informative.
u888vn – I appreciate how fast pages load and crisp content.
htechwebservice – Nice layout, content is clear and useful for web dev folks.
683tz084 – The layout is clean and easy to navigate.
fcalegacy – I find the resources extremely helpful and well organized.
seoelitepro – The content is diverse and engaging.
https://fixme.com.ua/
https://kiteschoolhurghada.ru/
Ich bin suchtig nach Snatch Casino, es ist eine dynamische Erfahrung. Die Optionen sind umfangreich und abwechslungsreich, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Service ist von bemerkenswerter Effizienz, antwortet in Sekundenschnelle. Die Transaktionen sind zuverlassig, jedoch mehr variierte Boni waren toll. Zum Schluss Snatch Casino garantiert eine top Spielerfahrung fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Spa? ! Zusatzlich die Oberflache ist flussig und modern, fugt Komfort zum Spiel hinzu.
snatch casino gr|
newstoday – Their local section is excellent, covers news I actually care about.
Сео аудит бесплатно онлайн https://seo-audit-sajta.ru
Need TRON Energy? buy tron energy instantly and save on TRX transaction fees. Rent TRON Energy quickly, securely, and affordably using USDT, TRX, or smart contract transactions. No hidden fees—maximize the efficiency of your blockchain.
https://yurhelp.in.ua/
cyrusmining – Might be a cloud-mining project, but transparency isn’t clear yet.
wraoys – Just visited, the layout is very minimal and seems sort of placeholder.
antsmarket – The website might even be for sale or parked currently.
Je suis integre a Mafia Casino, on complote un reseau de tactiques astucieuses. Les operations forment un plan de manigances innovantes, proposant des crash pour des chutes de pouvoir. L’assistance murmure des secrets nets, chuchotant des solutions claires et rapides. Les butins affluent via Bitcoin ou Ethereum, malgre cela des largesses gratuites supplementaires boosteraient les operations. En apotheose mafieuse, Mafia Casino forge une legende de jeu gangster pour les gardiens des empires numeriques ! En pot-de-vin supplementaire le graphisme est un complot dynamique et immersif, incite a prolonger l’intrigue infinie.
mafia 3 vargas casino|
axin2 – I like the font choices here, very readable and neat.
dhpb-smile – The layout is clean though minimal—could benefit from richer visuals.
saltburn – Right now it’s just a shell; content will make or break it later.
thefreemath – It’s inspiring to see free math content done well and with care.
liveforextrading – Very intuitive interface, even for someone new to forex.
귀하는 정말 흥미롭습니다! 이런 것을 전에 통해 읽은 적이 없다고 생각합니다.
이 이슈에 대해 유니크한 생각을 가진 누군가을 발견해서
정말 좋습니다. 이 사이트는 웹에서 요구되는 것입니다, 약간의 독창성을 가진 사람입니다!
Hello to every single one, it’s truly a nice for me to visit this website,
it contains important Information.
artvoyage – Their visual storytelling is compelling, it draws me back often.
live-sex-cam – The interface works perfectly, easy to navigate and enjoyable vibes.
googlerankmaster – This site has a cool name, hope the content lives up to it.
Need porn videos or photos? porn pen – create erotic content based on text descriptions. Generate porn images, videos, and animations online using artificial intelligence.
crowltheselinks – Offers look vague, would like to see clearer descriptions.
IPTV форум vip-tv.org.ua место, где обсуждают интернет-телевидение, делятся рабочими плейлистами, решают проблемы с плеерами и выбирают лучшие IPTV-сервисы. Присоединяйтесь к сообществу интернет-ТВ!
Ich habe einen totalen Hang zu SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit Spielen, die fur Kryptos optimiert sind. Der Service ist von hoher Qualitat, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, gelegentlich mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Daruber hinaus die Site ist schnell und stylish, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Besonders toll die Community-Events, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Ich liebe die Atmosphare von NV Casino, es bietet eine Reise voller Spannung. Es gibt eine beeindruckende Auswahl an Optionen, inklusive aufregender Sportwetten. Die Hilfe ist effizient und professionell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, ab und zu mehr abwechslungsreiche Boni waren willkommen. Zusammengefasst, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist kinderleicht, fugt eine Prise Magie hinzu.
playnvcasino.de|
wexfordliteraryartsfestival – This could really streamline the process of art authentication.
Ich bin total fasziniert von Snatch Casino, es liefert ein aufregendes Abenteuer. Es gibt eine unglaubliche Vielfalt an Spielen, mit Tausenden von Crypto-freundlichen Spielen. Der Service ist von bemerkenswerter Effizienz, erreichbar jederzeit. Die Gewinne kommen schnell, trotzdem zusatzliche Belohnungen waren top. Zum Schluss Snatch Casino ist eine au?ergewohnliche Plattform fur Crypto-Liebhaber ! Zusatzlich das Design ist ansprechend und intuitiv, macht jede Session immersiv.
snatch casino codice promo|
whollywoodhalloween – Nice touch with the dark theme, it feels professionally spooky too.
ukrainianvictoryisthebestaward – Nice branding, hope the content supports the weight of the name.
successmarketboutique – The idea of a global art registry feels like a game-changer.
janetfortampa – Excited to see how this evolves in the art community.
Je suis integre a Mafia Casino, il orchestre une conspiration de recompenses secretes. Il pullule d’une legion de complots interactifs, incluant des roulettes pour des tours de table. Le suivi protege avec une omerta absolue, avec une ruse qui anticipe les traitrises. Le protocole est ourdi pour une fluidite exemplaire, a l’occasion davantage de pots-de-vin bonus quotidiens renforceraient l’empire. En apotheose mafieuse, Mafia Casino forge une legende de jeu gangster pour les conspirateurs de victoires rusees ! De surcroit le graphisme est un complot dynamique et immersif, ce qui propulse chaque pari a un niveau de don.
mafia online casino|
Всё о металлообработке https://j-metall.ru и металлах: технологии, оборудование, сплавы и производство. Советы экспертов, статьи и новости отрасли для инженеров и производителей.
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es liefert ein Abenteuer voller Energie. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit dynamischen Tischspielen. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, verfugbar rund um die Uhr. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, ab und an regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino ist absolut empfehlenswert fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Nicht zu vergessen die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, verstarkt die Immersion. Hervorzuheben ist die Community-Events, die Vertrauen schaffen.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Ich habe eine Leidenschaft fur NV Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Wirbel aus Freude. Es wartet eine Fulle an spannenden Spielen, mit Spielen, die perfekt fur Kryptos geeignet sind. Der Support ist von herausragender Qualitat, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Der Prozess ist unkompliziert, manchmal die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Insgesamt, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Spieler auf der Suche nach Action ! Daruber hinaus die Navigation ist kinderleicht, was jede Session noch spannender macht.
playnvcasino.de|
לא עלה וזהו. הבנתי שאם הוא היה יודע, הוא לא היה יכול לשתוק. דרך דירות דיסקרטיות התחלתי ימים אלינה … משהו קרה לה. המבט שלה, הניצוצות בעיניה הירוקות, החיוך הקל קטיה, מבלי להסיר את עיניה, home
https://kiteschoolhurghada.ru/
Хочешь сдать металл? прием металла цена наша компания специализируется на профессиональном приёме металлолома уже на протяжении многих лет. За это время мы отточили процесс работы до совершенства и готовы предложить вам действительно выгодные условия сотрудничества. Мы принимаем практически любые металлические изделия: от небольших профилей до крупных металлоконструкций.
Есть металлолом? скупка металлолома цена мы предлагаем полный цикл услуг по приему металлолома в Санкт-Петербурге, включая оперативную транспортировку материалов непосредственно на перерабатывающий завод. Особое внимание мы уделяем удобству наших клиентов. Процесс сдачи металлолома организован максимально комфортно: осуществляем вывоз любых объемов металлических отходов прямо с вашей территории.
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites I stumbleupon every day. It will always be helpful to read content from other writers and practice a little something from their sites.
https://usadba.in.ua/chy-potribna-pichka-dlia-far-pry-vstanovlenni-bi-led-linz.html
Je suis totalement enchante par Bingoal Casino, on percoit une vitalite dechainee. Le repertoire est luxuriant et multifacette, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Le service est operationnel 24/7, assurant un support premium. Les retraits sont realises promptement, bien que plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. Globalement, Bingoal Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que le site est veloce et seduisant, intensifie le plaisir du jeu. Egalement notable le programme de fidelite avec des niveaux VIP, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Voir l’offre|
tripskan Tripskan – является вариантом написания названия “TripScan” с ошибкой. Несмотря на неточность, пользователь, скорее всего, ищет информацию о сервисе, связанном с путешествиями, планированием поездок, поиском и бронированием билетов и отелей. Опечатка указывает на возможное незнание точного названия интересующей платформы.
Ich kann nicht genug bekommen von NV Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Wirbel aus Freude. Der Katalog ist reich und vielfaltig, mit dynamischen Live-Sessions. Die Mitarbeiter reagieren blitzschnell, immer bereit zu helfen. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und flussig, manchmal die Angebote konnten gro?zugiger sein. Zusammengefasst, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Fans von Online-Wetten ! Nicht zu vergessen die Site ist schnell und elegant, macht die Erfahrung flussiger.
playnvcasino.de|
Je suis accro a Locowin Casino, il procure une odyssee unique. Il y a une multitude de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Les agents repondent avec celerite, toujours disponible pour assister. Les retraits sont effectues rapidement, mais quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. En bref, Locowin Casino offre une experience inoubliable pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Ajoutons que la plateforme est visuellement impressionnante, incite a prolonger l’experience. Un autre point fort les paiements securises en crypto, offre des recompenses continues.
Lire maintenant|
J’apprecie l’atmosphere de Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, assurant un support premium. Les benefices arrivent sans latence, cependant des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Globalement, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, stimule le desir de revenir. Particulierement attractif les paiements securises en crypto, qui stimule l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir|
Je suis surpris par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, incluant des paris sportifs electrisants. Pour un lancement puissant. Le service est operationnel 24/7, assurant un support premium. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, cependant plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! A mentionner la navigation est simple et engageante, stimule le desir de revenir. Un plus significatif les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sens de communaute.
Obtenir des infos|
Путешествуйте по Крыму https://м-драйв.рф на джипах! Ай-Петри, Ялта и другие живописные маршруты. Безопасно, интересно и с профессиональными водителями. Настоящий отдых с приключением!
Hello to every body, it’s my first pay a quick visit of this blog; this blog carries awesome and in fact good stuff in support of readers.
lee bet регистрация
Нужна карта? цена карты зарубежного банка как оформить зарубежную банковскую карту Visa или MasterCard для россиян в 2025 году. Карту иностранного банка можно открыть и получить удаленно онлайн с доставкой в Россию и другие страны. Зарубежные карты Visa и MasterCard подходят для оплаты за границей. Иностранные банковские карты открывают в Киргизии, Казахстане, Таджикистане и ряде других стран СНГ, все подробности смотрите по ссылке.
tripskan Tripscan трипскан: Двуязычное написание названия указывает на глобальный охват и мультиязычность платформы для путешественников, готовой предоставлять свои услуги как англоязычной, так и русскоязычной аудитории. TripScan/Трипскан представляет собой универсальную платформу, которая предоставляет всестороннюю поддержку путешественникам, независимо от их языка и местоположения. Сервис объединяет в себе возможности поиска и сравнения цен на авиабилеты, отели и прочие туристические услуги, а также предлагает инструменты для планирования маршрутов, создания персональных туров и обмена опытом с другими путешественниками. TripScan/Трипскан стремится быть незаменимым помощником в организации поездок, предлагая удобный интерфейс, персонализированные рекомендации и круглосуточную поддержку клиентов, чтобы каждое путешествие было максимально комфортным, безопасным и незабываемым. Платформа постоянно развивается и добавляет новые функции, чтобы соответствовать меняющимся потребностям путешественников и оставаться лидером в индустрии онлайн-туризма.
Металлообработка и металлы https://j-metall.ru/ ваш полный справочник по технологиям и материалам: обзоры станков и инструментов, таблицы марок и ГОСТов, кейсы производства, калькуляторы, вакансии, и свежие новости и аналитика отрасли для инженеров и закупщиков.
Строительный портал https://repair-house.kiev.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Подробные статьи, обзоры материалов, советы экспертов, новости отрасли и современные технологии для профессионалов и домашних мастеров.
Строительный портал https://intellectronics.com.ua источник актуальной информации о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Обзоры, инструкции, технологии, проекты и советы для профессионалов и новичков.
Портал о стройке https://mr.org.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Статьи, советы экспертов, современные технологии и обзоры материалов. Полезная информация для мастеров, инженеров и владельцев домов.
Актуальный портал https://sinergibumn.com о стройке и ремонте. Современные технологии, материалы, решения для дома и бизнеса. Полезные статьи, инструкции и рекомендации экспертов.
Женский портал https://prins.kiev.ua всё о красоте, моде, отношениях, здоровье и саморазвитии. Полезные советы, вдохновение, психология и стиль жизни для современных женщин.
Онлайн женский портал https://replyua.net.ua секреты красоты, стиль, любовь, карьера и семья. Читайте статьи, гороскопы, рецепты и советы для уверенных, успешных и счастливых женщин.
Современный женский https://novaya.com.ua портал о жизни, моде и гармонии. Уход за собой, отношения, здоровье, рецепты и вдохновение для тех, кто хочет быть красивой и счастливой каждый день.
Интересный женский https://muz-hoz.com.ua портал о моде, психологии, любви и красоте. Полезные статьи, тренды, рецепты и лайфхаки. Живи ярко, будь собой и вдохновляйся каждый день!
Женский портал https://z-b-r.org ваш источник идей и вдохновения. Советы по красоте, стилю, отношениям, карьере и дому. Всё, что важно знать современной женщине.
gmc цена купить бмв в москве – это приобрести автомобиль премиум-класса у официального дилера в Москве, который обеспечит высокий уровень сервиса и гарантийное обслуживание.
Софосбувир и велпатасвир цена Софосбувир: Современный Прорыв в Лечении Гепатита C Софосбувир – это инновационный противовирусный препарат, произведший революцию в лечении гепатита C. Он является ингибитором РНК-полимеразы вируса, что позволяет эффективно подавлять размножение вируса в организме. Софосбувир, как правило, используется в комбинации с другими противовирусными препаратами, такими как даклатасвир, ледипасвир или велпатасвир, для достижения высокой эффективности лечения. Софосбувир купить можно в специализированных аптеках или у официальных дистрибьюторов. Препарат обладает хорошей переносимостью и минимальными побочными эффектами. Цена на софосбувир может варьироваться в зависимости от производителя и места приобретения. Комбинация софосбувир и даклатасвир – это один из наиболее распространенных и эффективных режимов лечения гепатита C. Приобретение софосбувира и других препаратов следует осуществлять только по назначению врача и под его контролем. На сайтах, таких как Galaxy russ24 ru, gepatit stop, india helps24, можно найти информацию о препарате и возможности его приобретения. Однако, перед покупкой необходимо убедиться в подлинности и качестве препарата.
Онлайн авто портал https://retell.info всё для автолюбителей! Актуальные новости, обзоры новинок, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и полезные советы по эксплуатации и обслуживанию автомобилей.
Автомобильный портал https://autoguide.kyiv.ua для водителей и поклонников авто. Новости, аналитика, обзоры моделей, сравнения, советы по эксплуатации и ремонту машин разных брендов.
Авто портал https://psncodegeneratormiu.org мир машин в одном месте. Читайте обзоры, следите за новостями, узнавайте о новинках и технологиях. Полезный ресурс для автолюбителей и экспертов.
Авто портал https://bestsport.com.ua всё об автомобилях: новости, обзоры, тест-драйвы, советы по уходу и выбору машины. Узнайте о новинках автопрома, технологиях и трендах автомобильного мира.
Современный авто портал https://necin.com.ua мир автомобилей в одном месте. Тест-драйвы, сравнения, новости автопрома и советы экспертов. Будь в курсе последних тенденций автоиндустрии
автомобиль lexus hyundai москва – Hyundai в Москве предлагает широкий выбор автомобилей, от компактных хэтчбеков до вместительных внедорожников, с современным дизайном, передовыми технологиями и привлекательными ценами.
Ich bin komplett hin und weg von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit aufregenden Sportwetten. Die Agenten sind blitzschnell, mit praziser Unterstutzung. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, dennoch mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Zusatzlich die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Hervorzuheben ist die Vielfalt an Zahlungsmethoden, die Flexibilitat bieten.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
J’aime l’environnement distinct de Bingoal Casino, il procure une odyssee incomparable. Il existe une abondance de jeux envoutants, comprenant des jeux optimises pour les cryptos. Associe a des paris gratuits. Le suivi est exemplaire, toujours pret a intervenir. Les operations sont solides et veloces, par moments plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. Tout compte fait, Bingoal Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! En outre la navigation est simple et engageante, stimule le desir de revenir. Particulierement attractif les paiements securises en crypto, renforce le sens de communaute.
Cliquer et voir|
Портал про стройку https://dcsms.uzhgorod.ua всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне. Полезные советы, статьи, технологии, материалы и оборудование. Узнайте о современных решениях для дома и бизнеса.
Строительный портал https://msc.com.ua о ремонте, дизайне и технологиях. Полезные советы мастеров, обзоры материалов, новинки рынка и идеи для дома. Всё о стройке — от фундамента до отделки. Учись, строй и вдохновляйся вместе с нами!
Портал про стройку https://keravin.com.ua и ремонт полезные статьи, инструкции, обзоры оборудования и материалов. Всё о строительстве домов, дизайне и инженерных решениях
Онлайн-портал про стройку https://donbass.org.ua и ремонт. Новости, проекты, инструкции, обзоры материалов и технологий. Всё, что нужно знать о современном строительстве и архитектуре.
Je suis entierement obsede par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, avec des slots au style innovant. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. L’aide est performante et experte, proposant des reponses limpides. La procedure est aisee et efficace, mais des bonus plus diversifies seraient souhaitables. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! Par ailleurs la navigation est simple et engageante, facilite une immersion complete. Particulierement attractif les options de paris sportifs etendues, renforce le sens de communaute.
DГ©couvrir la page|
Je suis hypnotise par Casinia Casino, on ressent une energie fastueuse. Le repertoire est riche et varie, offrant des sessions live captivantes. Renforcant votre tresor initial. Le service est disponible 24/7, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient sublimes. En bref, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui trone en maitre pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! En bonus la navigation est intuitive comme un edit, incite a prolonger l’experience. Un atout cle le programme VIP avec 5 rangs princiers, cree une communaute vibrante.
Lire le guide|
Подоконники из искусственного камня https://luchshie-podokonniki-iz-kamnya.ru в Москве. Рейтинг лучших подоконников – авторское мнение, глубокий анализ производителей.
Je suis impressionne par Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, offrant des sessions live intenses. Le bonus d’accueil est attractif. Le suivi est exemplaire, toujours pret a intervenir. Les retraits sont realises promptement, par moments des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Tout compte fait, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les adeptes de sensations intenses ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, ajoute un confort notable. Un autre avantage cle les options de paris sportifs etendues, qui stimule l’engagement.
Continuer Г lire|
I’m profoundly fascinated by Wazamba Casino, it constructs an enthralling narrative. The varieties are comprehensive and layered, designed for digital currency operations. Heightening preliminary involvement. Help desk is remarkable. Benefits are conveyed rapidly, periodically further advantages would stand out. Concluding , Wazamba Casino turns essential for devotees for staking experts ! Moreover traversal is innate, augmenting each instance’s charm. Significant is obtaining elements for privileges, developing group cohesion.
https://wazambagr.com/|
Советы по строительству https://vodocar.com.ua и ремонту своими руками. Пошаговые инструкции, современные технологии, идеи для дома и участка. Мы поможем сделать ремонт проще, а строительство — надёжнее!
Сайт о строительстве https://valkbolos.com и ремонте домов, квартир и дач. Полезные советы мастеров, подбор материалов, дизайн-идеи, инструкции и обзоры инструментов. Всё, что нужно для качественного ремонта и современного строительства!
Полезный сайт https://stroy-portal.kyiv.ua о строительстве и ремонте: новости отрасли, технологии, материалы, интерьерные решения и лайфхаки от профессионалов. Всё для тех, кто строит, ремонтирует и создаёт уют.
Строительный сайт https://teplo.zt.ua для тех, кто создаёт дом своей мечты. Подробные обзоры, инструкции, подбор инструментов и дизайнерские проекты. Всё о ремонте и строительстве в одном месте.
Информационный портал https://smallbusiness.dp.ua про строительство, ремонт и интерьер. Свежие новости отрасли, обзоры технологий и полезные лайфхаки. Всё, что нужно знать о стройке и благоустройстве жилья в одном месте!
I’m blown away by Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it delivers edge-of-your-seat tension. Dual bet options add layers of strategy, offering max wins up to 10,000x your stake. Mobile-optimized for on-the-go blasts. Live chat resolves issues in seconds, accessible via multiple channels. Low fees on high-volume wins, nonetheless more bonus rounds could add variety. Wrapping it up, Astronaut Crash is a game-changer in crash titles for strategy lovers ! On top of that the visuals are sleek and spacey, simplifying bet adjustments. Notably tournaments for competitive crashes, lets you test strategies risk-free.
astronaut-crashgame777.com|
машина audi авто мерседес – Mercedes-Benz – это символ роскоши, комфорта и передовых технологий, предлагающий широкий выбор моделей для самых взыскательных клиентов.
Строим и ремонтируем https://buildingtips.kyiv.ua своими руками! Инструкции, советы, видеоуроки и лайфхаки для дома и дачи. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить бюджет.
Энциклопедия строительства https://kero.com.ua и ремонта: материалы, технологии, интерьерные решения и практические рекомендации. От фундамента до декора — всё, что нужно знать домовладельцу.
Пошаговые советы https://tsentralnyi.volyn.ua по строительству и ремонту. Узнай, как выбрать материалы, рассчитать бюджет и избежать ошибок. Простые решения для сложных задач — строим и ремонтируем с уверенностью!
Новостной портал https://kiev-online.com.ua с проверенной информацией. Свежие события, аналитика, репортажи и интервью. Узнавайте новости первыми — достоверно, быстро и без лишнего шума.
Главные новости дня https://sevsovet.com.ua эксклюзивные материалы, горячие темы и аналитика. Мы рассказываем то, что действительно важно. Будь в курсе вместе с нашим новостным порталом!
Simferopol Металло Строительство Металло строительство – это современное и эффективное решение для строительства зданий и сооружений различного назначения, от промышленных комплексов и торговых центров до жилых домов и офисных зданий. Наша компания предлагает полный спектр услуг по металло строительству, включая проектирование, изготовление, монтаж и отделку зданий. Мы используем высококачественный металлопрокат и современные технологии строительства, обеспечивающие прочность, надежность и долговечность зданий. Наши здания могут быть утеплены сэндвич-панелями или другими материалами, обеспечивающими комфортные условия эксплуатации в любое время года. Мы предлагаем широкий выбор архитектурных решений, позволяющих создать уникальный и привлекательный внешний вид здания. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете современное, надежное и экономичное решение для вашего бизнеса.
трансы Владивосток</a В культурах по всему миру трансовые состояния традиционно использовались для достижения духовного просветления, общения с духами, исцеления и разрешения личных проблем. Шаманы и жрецы, часто с помощью ритуальных практик, вводили себя и других в транс для получения знаний, пророчеств и избавления от болезней. Эти техники и сегодня используются в некоторых традиционных обществах.
Строим и ремонтируем https://srk.kiev.ua грамотно! Инструкции, пошаговые советы, видеоуроки и экспертные рекомендации. Узнай, как сделать ремонт качественно и сэкономить без потери результата.
Строительный портал https://sitetime.kiev.ua для мастеров и подрядчиков. Новые технологии, материалы, стандарты, проектные решения и обзоры оборудования. Всё, что нужно специалистам стройиндустрии.
Обустраивайте дом https://stroysam.kyiv.ua со вкусом! Современные идеи для ремонта и строительства, интерьерные тренды и советы по оформлению. Создайте стильное и уютное пространство своими руками.
Сайт о стройке https://samozahist.org.ua и ремонте для всех, кто любит уют и порядок. Расскажем, как выбрать материалы, обновить интерьер и избежать ошибок при ремонте. Всё просто, полезно и по делу.
Как построить https://rus3edin.org.ua и отремонтировать своими руками? Пошаговые инструкции, простые советы и подбор инструментов. Делаем ремонт доступным и понятным для каждого!
blsp at Приготовься узнать, что взорвало тёмные глубины интернета. Blacksprut – это не просто бренд. Это новый эталон анонимности, головокружительной скорости и абсолютной надежности в онлайн-мире. Посети bs2best.at – место, где раскрывают секреты, о которых другие даже шепотом боятся говорить. Ты получишь эксклюзивный доступ к данным, которые тщательно скрывают от непосвященных. Только для тех, кто в теме и готов к большему. Ни одного следа в сети, никаких уступок – только бескомпромиссная анонимность с Blacksprut. Не упусти эту уникальную возможность – стань одним из первых, кто узнает правду. bs2best.at уже ждёт тебя. Готов ли ты увидеть то, что скрыто от большинства?
AI ChatBot WordPress
Мужской сайт https://rkas.org.ua о жизни без компромиссов: спорт, путешествия, техника, карьера и отношения. Для тех, кто ценит свободу, силу и уверенность в себе.
Портал для автомобилистов https://translit.com.ua от выбора машины до профессионального ремонта. Читайте обзоры авто, новости автоспорта, сравнивайте цены и характеристики. Форум автолюбителей, советы экспертов и свежие предложения автосалонов.
Сайт для женщин https://oun-upa.org.ua которые ценят себя и жизнь. Мода, советы по уходу, любовь, семья, вдохновение и развитие. Найди идеи для новых свершений и будь самой собой в мире, где важно быть уникальной!
Мужской онлайн-журнал https://cruiser.com.ua о современных трендах, технологиях и саморазвитии. Мы пишем о том, что важно мужчине — от мотивации и здоровья до отдыха и финансов.
Ваш гид в мире https://nerjalivingspace.com автомобилей! Ежедневные авто новости, рейтинги, тест-драйвы и советы по эксплуатации. Найдите идеальный автомобиль, узнайте о страховании, кредитах и тюнинге.
J’ai une passion intense pour Bingoal Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. Il existe une profusion de jeux captivants, avec des slots innovants et thematises. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 200 €. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, par moments plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En fin de compte, Bingoal Casino garantit du divertissement constant pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! En outre le site est veloce et seduisant, ce qui eleve chaque session a un niveau superieur. Un plus significatif les options de paris sportifs etendues, renforce le sens de communaute.
Regarder maintenant|
Je suis ebloui par Bingoal Casino, il offre une odyssee incomparable. Le repertoire est luxuriant et multifacette, offrant des sessions live intenses. Le bonus d’inscription est seduisant. Le suivi est exemplaire, assurant un support premium. Les operations sont solides et veloces, de temps a autre plus de promotions frequentes seraient un atout. En synthese, Bingoal Casino fournit une experience ineffacable pour les enthousiastes de casino en ligne ! De surcroit le design est contemporain et lisse, ajoute un confort notable. Particulierement attractif les options de paris sportifs etendues, qui stimule l’engagement.
Tout apprendre|
Ялта Изготовление Металлоконструкций Изготовление металлоконструкций – это сложный и технологически емкий процесс, требующий высокой квалификации персонала и современного оборудования. Наша компания специализируется на изготовлении металлоконструкций любой сложности, включая каркасы зданий, фермы, балки, колонны, резервуары, технологические трубопроводы и другие металлоизделия. Мы используем современные технологии резки, сварки, гибки и обработки металла, обеспечивающие точность и соответствие требованиям действующих стандартов. Наша команда опытных специалистов обеспечивает контроль качества на всех этапах производства, от входного контроля сырья до отгрузки готовой продукции. Выбирая нас, вы выбираете качество и надежность ваших металлоконструкций.
J’ai une passion debordante pour Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais scintillant. L’eventail de jeux est resplendissant, proposant des jeux de table raffines. L’offre de bienvenue est eclatante. L’assistance est rapide et precise, joignable a toute heure. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de la lumiere, cependant quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient lumineux. En bref, Casinia Casino est un joyau pour les joueurs pour les passionnes de frissons lumineux ! De plus le design est moderne et eblouissant, incite a prolonger l’aventure. Particulierement captivant les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions fiables.
Essayer d’explorer|
Je suis emerveille par Casinia Casino, c’est une plateforme qui brille d’une energie lumineuse. Il y a une profusion de jeux envoutants, offrant des sessions live captivantes. 100% jusqu’a 500 € + 200 tours gratuits. Le suivi est irreprochable, joignable a toute heure. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient scintillantes. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui illumine le jeu pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Ajoutons que la navigation est intuitive comme une lueur, ce qui rend chaque session plus eclatante. Particulierement captivant les paiements securises en crypto, propose des recompenses sur mesure.
Commencer Г lire|
Je suis captive par Casinia Casino, c’est une plateforme qui rayonne de luxe. La variete des titres est majestueuse, incluant des paris sportifs dynamiques. Renforcant votre capital initial. L’assistance est efficace et courtoise, offrant des reponses claires. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, neanmoins quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient bienvenus. Au final, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui regne en maitre pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Cerise sur le gateau la navigation est simple et agreable, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus royale. A noter egalement les tournois reguliers pour la competition, offre des recompenses continues.
Trouver la vГ©ritГ©|
Je suis totalement seduit par Locowin Casino, il offre une experience unique. Il y a une multitude de jeux excitants, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Pour un demarrage en force. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les gains arrivent sans delai, de temps en temps des offres plus genereuses ajouteraient du piquant. En bref, Locowin Casino vaut largement le detour pour les amateurs de sensations fortes ! De plus le site est rapide et attrayant, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. Un plus non negligeable les options de paris sportifs variees, offre des recompenses continues.
Commencer l’aventure|
трансы воронеж В контексте психотерапии, хорошие трансы, вызванные гипнозом или медитацией, служат мощным инструментом для работы с подсознанием, позволяют обойти рациональное сопротивление и обратиться к глубинным ресурсам психики. Они помогают в преодолении тревожных расстройств, фобий, зависимостей, способствуют проработке травматического опыта и облегчению хронической боли. Ключевую роль играет безопасная и поддерживающая обстановка, созданная терапевтом, и доверие пациента.
Портал о дизайне https://sculptureproject.org.ua интерьеров и пространства. Идеи, тренды, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и общественных мест. Советы дизайнеров и примеры стильных решений каждый день.
Строительный сайт https://okna-k.com.ua для профессионалов и новичков. Новости отрасли, обзоры материалов, технологии строительства и ремонта, советы мастеров и пошаговые инструкции для качественного результата.
Сайт о металлах https://metalprotection.com.ua и металлообработке: виды металлов, сплавы, технологии обработки, оборудование и новости отрасли. Всё для специалистов и профессионалов металлургии.
Главный автопортал страны https://nmiu.org.ua всё об автомобилях в одном месте! Новости, обзоры, советы, автообъявления, страхование, ТО и сервис. Для водителей, механиков и просто любителей машин.
Женский онлайн-журнал https://rosetti.com.ua о стиле, здоровье и семье. Новости моды, советы экспертов, тренды красоты и секреты счастья. Всё, что важно и интересно женщинам любого возраста.
bs2best at Заинтригован, что вызывает резонанс в тёмных закоулках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто наименование, это воплощение идеала анонимности, стремительной работы и непоколебимой уверенности. Отправляйся на bs2best.at — в обитель, где раскрывают секреты, о которых предпочитают молчать. Здесь тебе станет доступно сокровенное знание, охраняемое от непосвященных. Исключительно для тех, кто понимает суть. Никаких улик. Никаких соглашений. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти драгоценную возможность стать пионером — bs2best.at распахнул врата для тех, кто ищет истину. Хватит ли тебе отваги заглянуть правде в лицо?
I can’t resist the allure of Wazamba Casino, it unleashes a distinctive energy. There’s a vast spectrum of options, encompassing over 5,000 entries from premier developers. The introductory offer is appealing. Assistance team is superb. Cashouts are executed promptly, occasionally supplementary perks would excel. In totality, Wazamba Casino supplies premium leisure for excitement chasers ! Also exploration is natural, infusing added allure. A further advantage competitions for rivalry, delivering customized favors.
wazambagr.com|
I’m all in on Astronaut Crash by 100HP Gaming, it’s a pulse-racing voyage through the stars. Games wrap up in seconds for endless replays, showcasing a multiplier that escalates dramatically. Balanced volatility for steady thrills. Help desk is responsive and expert, upholding outcome transparency. Payouts zip through without hitches, now and again advanced auto-tools for vets. Taking stock, Astronaut Crash redefines crash gaming standards for multiplier maniacs ! Bonus speeds are blisteringly quick, layering sound for immersion. Highlight fairness audit tools, facilitates low-cost transfers.
https://astronaut-crashgame777.com/|
Студия ремонта https://anti-orange.com.ua квартир и домов. Выполняем ремонт под ключ, дизайн-проекты, отделочные и инженерные работы. Качество, сроки и индивидуальный подход к каждому клиенту.
Туристический портал https://feokurort.com.ua для любителей путешествий! Страны, маршруты, достопримечательности, советы и лайфхаки. Планируйте отдых, находите вдохновение и открывайте мир вместе с нами.
video talk
connectwiththeworldnow – The brand feels urgent, visuals add strength to the narrative.
telecharger 1xbet cameroun https://parifoot-afrique.com
Студия дизайна https://bathen.rv.ua интерьеров и архитектурных решений. Создаём стильные, функциональные и гармоничные пространства. Индивидуальный подход, авторские проекты и внимание к деталям.
1xbet afrique apk 1xbet cameroun apk
Ремонт и строительство https://fmsu.org.ua без лишних сложностей! Подробные статьи, обзоры инструментов, лайфхаки и практические советы. Мы поможем построить, отремонтировать и обустроить ваш дом.
pariez sur le foot football africain
Ich bin abhangig von SpinBetter Casino, es fuhlt sich an wie ein Strudel aus Freude. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, bietet klare Losungen. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, gelegentlich mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. Zusammengefasst, SpinBetter Casino garantiert hochsten Spa? fur Adrenalin-Sucher ! Hinzu kommt die Interface ist intuitiv und modern, gibt den Anreiz, langer zu bleiben. Ein weiterer Vorteil die schnellen Einzahlungen, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
Je suis captive par Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. La gamme de jeux est spectaculaire, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. Les agents reagissent avec promptitude, assurant un support premium. La procedure est aisee et efficace, de temps a autre quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. En synthese, Locowin Casino est essentiel pour les amateurs pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! De surcroit le design est contemporain et lisse, ajoute un confort notable. Egalement notable les tournois periodiques pour la rivalite, offre des privileges sur mesure.
Voir les dГ©tails|
адмирал икс
Je suis hypnotise par Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans une cour enchanteresse. Il y a une profusion de jeux captivants, comprenant des jeux compatibles avec les cryptos. Elevant l’experience de jeu. Le suivi est irreprochable, garantissant un service princier. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, parfois des recompenses additionnelles seraient imperiales. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino est un pilier pour les joueurs pour les amateurs de casino en ligne ! Par ailleurs le site est rapide et majestueux, incite a prolonger l’experience. Un atout cle les paiements securises en crypto, garantit des transactions fiables.
VГ©rifier ceci|
J’aime l’ambiance royale de Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais enchanteur. Les options sont vastes comme un royaume, offrant des sessions live immersives. Plus un Bonus Crab pour demarrer. Les agents repondent avec celerite, joignable a toute heure. Les retraits sont rapides comme l’eclair, cependant des recompenses additionnelles seraient royales. Dans l’ensemble, Casinia Casino vaut largement le detour pour les passionnes de jeux modernes ! Ajoutons que l’interface est intuitive et elegante, ce qui rend chaque session encore plus royale. Un plus non negligeable les tournois reguliers pour la competition, assure des transactions fiables.
Apprendre la mГ©thode|
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, il delivre une experience unique. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, offrant des sessions live intenses. Associe a des tours gratuits sans wager. L’aide est performante et experte, avec une assistance exacte et veloce. Les operations sont solides et veloces, cependant des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Globalement, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! Par ailleurs la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, ajoute un confort notable. Particulierement attractif le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, renforce le sens de communaute.
Apprendre les secrets|
https://bs2tsite3.lat
https://sabina.develop-blog.com/45360397/1xbet-bd-promo-code-new-user-bonus-100-up-to-130
Hi there! I realize this is kind of off-topic but I had to ask. Does running a well-established website like yours require a lot of work? I’m completely new to writing a blog but I do write in my diary everyday. I’d like to start a blog so I will be able to share my personal experience and views online. Please let me know if you have any recommendations or tips for new aspiring bloggers. Appreciate it!
https://kra41-cc.cc
адмирал икс казино
I’m addicted to Wazamba Casino, it unleashes a special vibe. The library is truly enormous, boasting over 5,000 games from 100+ providers. The sign-up bonus is enticing. Support team is exceptional. Operations are straightforward, at times additional incentives would shine. In summary, Wazamba Casino provides elite entertainment for gaming aficionados ! Additionally the visuals are captivating and immersive, streamlining user experience. Another standout feature VIP tiers with exclusive privileges, building community engagement.
wazambagr.com|
камера полимеризации порошковой краски купить Печь для порошковой покраски в Санкт-Петербурге (СПб) – это термическое оборудование, предназначенное для полимеризации порошковых красок, нанесенных на металлические изделия, с целью создания прочного и долговечного покрытия. В Санкт-Петербурге представлен широкий ассортимент печей для порошковой покраски, от небольших камер полимеризации для малых предприятий и мастерских, до крупногабаритных проходных печей для промышленных линий. При выборе печи необходимо учитывать размеры обрабатываемых изделий, требуемую производительность, тип используемой порошковой краски и бюджет. В СПб можно найти печи как от отечественных, так и от зарубежных производителей. Важно обратить внимание на теплоизоляцию печи, равномерность распределения температуры внутри камеры, тип нагревательных элементов (электрические, газовые, дизельные) и наличие системы управления с возможностью программирования режимов полимеризации. Также стоит учитывать энергоэффективность печи и возможность ее интеграции в существующую линию порошковой покраски. Покупка печи для порошковой покраски в СПб – это важный шаг для любого предприятия, занимающегося обработкой металла, и требует тщательного анализа потребностей и возможностей.
Современная студия дизайна https://bconline.com.ua архитектура, интерьер, декор. Мы создаём пространства, где технологии сочетаются с красотой, а стиль — с удобством.
telecharger 1xbet cameroun parier foot en ligne
pronostic foot gratuit telecharger 1xbet cameroun
pronostics du foot telecharger 1xbet pour android
Создавайте дом https://it-cifra.com.ua своей мечты! Всё о строительстве, ремонте и дизайне интерьера. Идеи, проекты, фото и инструкции — вдохновляйтесь и воплощайте задуманное легко и с удовольствием.
stamps worth money
auf casino рабочее зеркало
https://m-bsme.lat
ascendgrid – Good domain name, memorable and brandable for sure.
https://t.me/tripscan_1
bs2best зеркало Заинтригован, что вызывает резонанс в тёмных закоулках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто наименование, это воплощение идеала анонимности, стремительной работы и непоколебимой уверенности. Отправляйся на bs2best.at — в обитель, где раскрывают секреты, о которых предпочитают молчать. Здесь тебе станет доступно сокровенное знание, охраняемое от непосвященных. Исключительно для тех, кто понимает суть. Никаких улик. Никаких соглашений. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти драгоценную возможность стать пионером — bs2best.at распахнул врата для тех, кто ищет истину. Хватит ли тебе отваги заглянуть правде в лицо?
social stream
truelaunch – Impressed by the practical ideas, not just theories.
brandvision – Great branding ideas, I’m noting them down for my own work.
1xslots casino
purehorizon – Bookmarking this right now, I’ll definitely revisit.
innovatek – Really like their tech breakdowns, super clear and helpful.
электрокарнизы для штор купить электрокарнизы для штор купить .
проект перепланировки нежилого помещения стоимость http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya10.ru/ .
работа экскаватора цена за час работа экскаватора цена за час .
Мир архитектуры https://vineyardartdecor.com и дизайна в одном месте! Лучшие идеи, проекты и вдохновение для дома, офиса и города. Узнай, как создаются красивые и функциональные пространства.
согласование проекта перепланировки нежилого помещения pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya11.ru .
1xslots зеркало
valuevision – I’ll check back later to see updates, this has potential.
согласование перепланировки нежилого помещения в москве http://www.pereplanirovka-nezhilogo-pomeshcheniya9.ru/ .
growthverse – Great user experience, everything loads so smoothly and fast.
трипскан
Ich bin fasziniert von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Der Katalog ist reichhaltig und variiert, mit innovativen Slots und fesselnden Designs. Die Hilfe ist effizient und pro, bietet klare Losungen. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und smooth, dennoch regelma?igere Aktionen waren toll. Global gesehen, SpinBetter Casino bietet unvergessliche Momente fur Online-Wetten-Fans ! Daruber hinaus die Site ist schnell und stylish, verstarkt die Immersion. Besonders toll die mobilen Apps, die den Spa? verlangern.
https://spinbettercasino.de/|
J’aime l’atmosphere unique de Locowin Casino, ca offre un thrill incomparable. Le catalogue est abondant et multifacette, offrant des sessions live intenses. Amplifiant l’experience initiale. Le suivi est impeccable, toujours disponible pour assister. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, cependant plus de promos regulieres seraient un plus. Dans l’ensemble, Locowin Casino garantit du plaisir a chaque instant pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! En bonus la navigation est simple et plaisante, amplifie le plaisir de jouer. Egalement appreciable les evenements communautaires engageants, offre des recompenses continues.
Apprendre la mГ©thode|
электро рулонные шторы http://rulonnaya-shtora-s-elektroprivodom.ru/ .
skyportal – User experience is smooth, links and menus work perfectly.
show experience
J’apprecie l’environnement de Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. La diversite des titres est epoustouflante, avec des slots au style innovant. Renforcant l’experience de depart. Le suivi est exemplaire, proposant des reponses limpides. Les retraits sont realises promptement, de temps a autre des offres plus liberales ajouteraient de la valeur. Pour synthetiser, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les aficionados de jeux contemporains ! En outre la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, facilite une immersion complete. Un autre avantage cle les paiements securises en crypto, qui stimule l’engagement.
DГ©couvrir le contenu|
smartgrid – Friendly branding choice, sounds modern and strong.
trendforge – The name suggests being ahead of trends; that’s appealing.
quantumreach – Clean layout, easy to navigate, very user-friendly experience.
Je suis stupefait par Locowin Casino, c’est une plateforme qui explose d’energie. Les alternatives sont incroyablement etendues, offrant des sessions live intenses. Pour un lancement puissant. L’equipe d’assistance est remarquable, accessible a tout instant. Les operations sont solides et veloces, bien que quelques tours gratuits supplementaires seraient apprecies. Globalement, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour ceux qui parient en crypto ! En outre la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, stimule le desir de revenir. Un plus significatif les evenements communautaires captivants, garantit des transactions securisees.
DГ©couvrir la page|
boldimpact – The domain looks strong, hoping content is up soon.
bluetrail – The content seems solid, gives a trustworthy impression so far.
alphaunity – The visuals complement the text nicely, very balanced design.
риобет казино
solidvision – Tried several times, page didn’t load yet.
sharpbridge – Navigation feels intuitive, didn’t struggle finding anything so far.
goldbridge – Overall promising — just needs more content to fill the promise.
I’m amazed by Wazamba Casino, it generates crazy gaming vibes. The selection of games is phenomenal, offering live dealer games that immerse you. The welcome bonus is generous. Professional and helpful assistance. Transactions are hassle-free, occasionally additional bonuses might be welcome. To sum up, Wazamba Casino provides guaranteed enjoyment for casino enthusiasts ! Additionally navigation is effortless, which heightens the fun of every session. Especially great tournaments for competitive play, ensuring secure transactions.
wazambagr.com|
elitegrowth – Offers valuable insights, and the interface is top-notch.
cloudmatrix – Found exactly what I was looking for, very intuitive.
fastgrowth – Navigation is seamless, and the visuals are appealing.
maxvision – Navigation is seamless, and the visuals are appealing.
greenmotion – The content is engaging, and the site is responsive.
zenithlabs – Love the clean design, really easy to navigate today.
boldnetwork – Found this by chance, curious what kind of content they’ll share.
thinkbeyondtech – A pleasure to browse, everything is well-organized and clear.
nextlayer – Offers valuable insights, and the interface is top-notch.
Estou completamente empolgado com BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura competitiva. O catalogo e rico e diversificado, oferecendo jogos de mesa dinamicos. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O suporte ao cliente e de elite, sempre pronto para o jogo. Os ganhos chegam sem demora, contudo recompensas extras seriam um hat-trick. No fim, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Alem disso o site e veloz e envolvente, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Notavel tambem os eventos comunitarios envolventes, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Ler mais|
focuslab – Impressed by their writing style and layout synergy.
анлим казино
urbanmatrix – Found some useful ideas I might try, the content feels practical.
growwithfocus – Expecting good visuals and easy-to-read layout here.
nextrealm – Tried loading the site, got an error but the branding feels strong.
openlaunch – The layout is clean and browsing feels smooth.
blueorbit – The visuals are crisp and the layout is very balanced.
1xslots рабочее зеркало
гребной тренажер oxygen Эллиптический тренажер купить — инвестиция в низкоударные тренировки. Орбитрек сочетает бег, ходьбу и степ, задействуя руки и ноги без нагрузки на суставы. Магнитная или электромагнитная нагрузка 16-32 уровня, длина шага 30-50 см для комфорта. Дисплей показывает скорость, пульс, калории, с предустановленными программами. Размеры 150×60 см, вес 30-50 кг, нагрузка 120-150 кг. Идеален для реабилитации, кардио и сжигания жира. Цены от 15 000 до 80 000 рублей, бренды Body Sculpture или Horizon. Эллипс укрепляет мышцы, улучшает баланс и повышает аэробную capacity.
bs market Интересуешься, что происходит в тёмных уголках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это гарантия анонимности, высокой скорости и надежности. Переходи на bs2best.at — там ты найдёшь то, о чём другие умалчивают. Тебе откроется доступ к информации, которую скрывают от большинства. Только для тех, кто понимает. Без компрометирующих следов. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти шанс узнать первым — bs2best.at уже готов открыть свои двери. Дерзнешь ли ты взглянуть правде в глаза?
https://bs2best.cat
Заботьтесь о здоровье сосудов ног с профессионалом! В группе «Заметки практикующего врача-флеболога» вы узнаете всё о профилактике варикоза, современных методиках лечения (склеротерапия, ЭВЛО), УЗИ вен и точной диагностике. Доверяйте опытному врачу — ваши ноги заслуживают лучшего: https://phlebology-blog.ru/
ynaix – Wow this site looks slick, very modern and impressive visuals.
connectwiththeworldnow – Navigation is smooth, found what I needed quickly.
strongrod – Navigation is solid, I found what I needed quickly.
Je suis epate par Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. Les options sont incroyablement vastes, offrant des sessions live dynamiques. Pour un demarrage en force. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les transactions sont fiables et rapides, cependant plus de promos regulieres seraient top. En bref, Locowin Casino vaut largement le detour pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! Cerise sur le gateau la plateforme est visuellement top, ajoute une touche de confort. A noter egalement les evenements communautaires engageants, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Commencer maintenant|
wavefusion – Really like the style here, feels fresh and creative.
sharpwave – Content feels high quality, very informative and credible overall.
brightideaweb – Layout is intuitive, reading flow is smooth and comfortable.
metarise – Content is high quality, I feel like I learned something solid.
Je suis fascine par Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, avec des slots au style innovant. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. L’aide est performante et experte, proposant des reponses limpides. Les operations sont solides et veloces, mais des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. En synthese, Locowin Casino est une plateforme qui excelle pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! En outre l’interface est intuitive et raffinee, facilite une immersion complete. Un autre avantage cle les options de paris sportifs etendues, garantit des transactions securisees.
Explorer tout|
cyberlaunch – The writing tone is confident yet friendly, good balance.
innovatewithus – Awesome ideas here, pushing creativity in every single post.
J’aime l’atmosphere de Locowin Casino, on detecte une vibe folle. Le repertoire est opulent et multifacette, comprenant des jeux adaptes aux cryptos. Doublement des depots jusqu’a 1850 €. L’aide est performante et experte, toujours pret a intervenir. Les paiements sont proteges et lisses, mais des incitations additionnelles seraient un benefice. En fin de compte, Locowin Casino merite une exploration approfondie pour les joueurs a la recherche d’aventure ! De surcroit la plateforme est esthetiquement remarquable, stimule le desir de revenir. Un autre avantage cle le programme VIP avec des niveaux exclusifs, propose des recompenses permanentes.
Naviguer sur le site|
brightchain – The tone feels authentic, not too formal or too casual.
bestchoiceonline – Images load fine, product descriptions are honest and detailed.
cloudmark – The homepage is elegant, feels welcoming and well-designed.
nextbrand – Looks sleek, very modern layout and clean with good contrast.
Частный заем денег домашние деньги займ на карту альтернатива банковскому кредиту. Быстро, безопасно и без бюрократии. Получите нужную сумму наличными или на карту за считанные минуты.
digitalstorm – The voice feels authentic, technical without being overwhelming.
https://bs2site4.io
discoveramazingthingsonline – Navigation is smooth, helped me stumble on cool things fast.
everythingyouneedtoknow – Overall very polished, feels like a high quality informational hub.
ultrawave – Color choices work well, read-ability is excellent throughout.
explorecreativeideasdaily – Color palette is refreshing, helps keep me motivated while browsing.
Все спортивные новости http://sportsat.ru в реальном времени. Итоги матчей, трансферы, рейтинги и обзоры. Следите за событиями мирового спорта и оставайтесь в курсе побед и рекордов!
велотренажер магнитный Велотренажер для дома — компактный и тихий тренажер для ежедневных тренировок. Вертикальные модели занимают мало места, с эргономичным сиденьем и регулируемыми педалями. Магнитная система обеспечивает бесшумную работу, идеальную для квартир. 8-24 уровня нагрузки для начинающих и продвинутых, с программами интервальной тренировки. Сенсоры на руле измеряют пульс, а компьютер показывает прогресс. Материал — сталь с антикоррозийным покрытием для долговечности. Подходит для похудения, тонизации мышц и профилактики варикоза. Бюджет от 8 000 рублей, с гарантией 1-3 года. Домашний велотренажер мотивирует к регулярным занятиям без погодных ограничений.
yourbrandzone – Pages load quickly without delays, very optimized experience.
pixelplanet – Tone is friendly and engaging without being overly casual or vague.
zenithmedia – Typography is crisp, spacing makes reading comfortable.
boldspark – Looks professional, gives confidence that the offerings are high quality.
bs2best зеркало Что, еще не слышал о сенсации, сотрясающей глубины даркнета? Blacksprut – это не просто торговая марка. Это ориентир в мире, где правят анонимность, скоростные транзакции и нерушимая надежность. Спеши на bs2best.at – там тебя ждет откровение, то, о чем многие умалчивают, предпочитая оставаться в тени. Ты получишь ключи к информации, тщательно оберегаемой от широкой публики. Только для тех, кто посвящен в суть вещей. Полное отсутствие следов. Никаких компромиссов. Лишь совершенство, имя которому Blacksprut. Не дай возможности ускользнуть – стань одним из первых, кто познает истину. bs2best.at уже распахнул свои объятия. Готов ли ты к встрече с реальностью, которая шокирует?
Estou alucinado com BR4Bet Casino, vibra como um farol em alto-mar. Os jogos formam um clarao de entretenimento. oferecendo sessoes ao vivo que reluzem como chamas. Os agentes sao rapidos como um raio de farol. assegurando apoio sem sombras. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. porem mais recompensas fariam o coracao brilhar. Na real, BR4Bet Casino promete uma diversao que e uma chama para os viciados em emocoes de cassino! De bonus a plataforma reluz com um visual brilhante. adicionando um toque de luz ao cassino.
br4bet e confiГЎvel|
futurebeam – Tone of writing is friendly and inspiring, not too generic.
Je trouve absolument cartoon Simsinos Casino, resonne avec un rythme de casino anime. Il y a une cascade de jeux de casino captivants. comprenant des jeux de casino adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le personnel du casino offre un accompagnement digne d’un scenariste. proposant un appui qui enchante. Les retraits au casino sont rapides comme un fondu. occasionnellement des tours gratuits pour une melodie coloree. En conclusion, Simsinos Casino c’est un casino a explorer sans tarder pour les amoureux des slots modernes de casino! Bonus resonne avec une melodie graphique toon. donne envie de replonger dans le casino sans fin.
simsinos casino|
Galera, preciso compartilhar minha experiencia no 4PlayBet Casino porque foi muito alem do que imaginei. A variedade de jogos e surreal: blackjack envolvente, todos sem travar. O suporte foi atencioso, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que passa seguranca. Fiz saque em PIX e o dinheiro entrou em minutos, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que podia ter mais promocoes semanais, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Resumindo, o 4PlayBet Casino tem diferencial real. Com certeza vou continuar jogando.
4play wheels 18 inch|
Estou completamente apaixonado por BETesporte Casino, leva a um universo de apostas dinamico. As opcoes sao amplas como um campo de futebol, com slots modernos e tematicos. Com uma oferta inicial para impulsionar. O acompanhamento e impecavel, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. As transacoes sao confiaveis, de vez em quando ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. Resumindo, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Tambem a plataforma e visualmente impactante, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Muito atrativo os eventos comunitarios envolventes, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Obter informações|
kluvcc – The content is engaging, helpful, and well-written.
Tenho uma paixao ardente por PlayPIX Casino, proporciona uma aventura pulsante. As opcoes sao amplas como um festival, com slots de design inovador. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, oferecendo respostas claras. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, de vez em quando promocoes mais frequentes dariam um toque extra. Para finalizar, PlayPIX Casino e essencial para jogadores para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Tambem a navegacao e intuitiva e envolvente, aumenta o prazer de jogar. Notavel tambem o programa VIP com niveis exclusivos, oferece recompensas continuas.
Saber mais|
broadcast zone
Suchen Sie Immobilien? montenegro-immobilien-kaufen.com wohnungen, Villen und Grundstucke mit Meerblick. Aktuelle Preise, Fotos, Auswahlhilfe und umfassende Transaktionsunterstutzung.
alphaimpact – Good contrast and color scheme; elements stand out clearly.
coreimpact – Navigation menu is intuitive, did not get lost once.
ideaorbit – The visual style is sleek, fonts and spacing sound perfect.
https://bs2tcite4.io
joinourcreativecommunity – Content is encouraging, makes me want to contribute and learn.
YourPathOfGrowth – I appreciate how they focus on sustainable solutions for all.
thebestplacetostarttoday – Navigation is clear, I didn’t waste time looking for things.
LearnWithConfidence – Their guides are thorough, I learned so much in minutes.
makingeverymomentcount – Design feels warm and personal, very inviting experience.
learnshareandsucceed – Love the mission here, seems like a place to really grow together.
getreadytoexplore – Design feels crisp, layout clean, visuals nicely balanced.
findwhatyouarelookingfor – Navigation feels intuitive, didn’t struggle to get around.
everythingaboutsuccess – Overall very polished experience, feels like a premium motivational hub.
learnsomethingneweveryday – I appreciate how clean and uncluttered the layout feels.
makelifebettereveryday – Feels like a place to find everyday inspiration and small wins.
discoverendlessinspiration – Color choices are beautiful, contrast and harmony felt throughout.
J’adore l’ambiance de Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. La selection de jeux est phenomenale, avec des slots au design innovant. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Le suivi client est irreprochable, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les gains arrivent sans delai, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino offre une experience memorable pour ceux qui aiment parier en crypto ! De plus la plateforme est visuellement top, donne envie de prolonger l’experience. A noter egalement les tournois reguliers pour la competition, renforce le sentiment de communaute.
Rejoindre maintenant|
growyourbusinessfast – Navigation is intuitive, got to what I needed quickly.
микрозайм онлайн
Появилась возможность пройти курс по биофизике чтобы работать на стыке биологии и физики и участвовать в research клеточных процессов, я взял микрозайм онлайн без процентов и освоил междисциплинарные подходы, деньги пришли быстро и я теперь работаю в университетской лаборатории где изучаю механизмы работы белков что позволяет мне вносить вклад в фундаментальную науку
J’adore l’eclat vibrant de Casinia Casino, ca transporte dans un palais scintillant. Les options sont vastes comme un ciel etoile, avec des slots aux designs audacieux et thematiques. L’offre de bienvenue est eclatante. Le suivi est irreprochable, avec une aide claire et veloce. Les gains arrivent a la vitesse de la lumiere, parfois des offres plus genereuses seraient un plus. En bref, Casinia Casino est une plateforme qui illumine le jeu pour les joueurs en quete d’eclat ! En bonus la navigation est intuitive comme une lueur, ce qui rend chaque session plus eclatante. Particulierement captivant les evenements communautaires captivants, garantit des transactions fiables.
Voir la liste complГЁte|
makeimpactwithideas – Content is meaningful, not just filler, gives real takeaways.
J’ai un coup de foudre pour Locowin Casino, ca transporte dans un monde captivant. La variete des titres est impressionnante, proposant des jeux de table immersifs. Le bonus de bienvenue est attractif. Le service est disponible 24/7, avec une aide precise et rapide. Les paiements sont securises et fluides, cependant des bonus plus varies seraient bienvenus. Pour conclure, Locowin Casino vaut largement le detour pour les joueurs en quete d’excitation ! Cerise sur le gateau le design est moderne et fluide, facilite une immersion totale. Un autre atout majeur les evenements communautaires engageants, propose des avantages personnalises.
Explorer plus|
https://djmathieug.com/cropped-foodiesfeed-com_get-ready-for-your-espresso-jpg/
GrowWithConfidenceHere – Navigation is smooth, finding resources for projects is super fast.
BuildSomethingMeaningful – The resources here are perfect for anyone looking to make a change.
SimpleWaysToBeHappy – Love how this site encourages daily gratitude practices.
TogetherWeCreateChange – Navigation is smooth, finding resources for projects is super fast.
YourTrustedSourceOnline – The resources here are perfect for anyone looking to make a change.
BuildABetterTomorrow – I love how they integrate technology into their initiatives.
CreateInspireAndGrow – The content here is top-notch, really helps me stay motivated.
stayupdatedwithtrends – Navigation is slick, finding what’s new is easy and quick.
**mindvault**
mindvault is a premium cognitive support formula created for adults 45+. It’s thoughtfully designed to help maintain clear thinking
**mindvault**
mindvault is a premium cognitive support formula created for adults 45+. It’s thoughtfully designed to help maintain clear thinking
Estou alucinado com PlayPix Casino, e um cassino online que reluz como um pixel em overclock. O catalogo de jogos e uma tela de emocoes. com caca-niqueis modernos que glitcham como retro. O time do cassino e digno de um programador. com ajuda que renderiza como um glitch. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. em alguns momentos mais giros gratis seriam uma loucura cibernetica. No fim das contas, PlayPix Casino e uma onda de adrenalina digital para os fas de adrenalina pixelada! Vale dizer o site e uma obra-prima de estilo digital. fazendo o cassino processar como um CPU.
quem Г© o dono da playpix|
discoveramazingstories – Overall feels inspiring; stories like this help connect and understand more.
Estou alucinado com Fogo777 Casino, e uma explosao de diversao que acende como uma pira. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados. com caca-niqueis modernos que hipnotizam como fogos. O servico e confiavel como uma fogueira. com ajuda que ilumina como uma pira. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos. mas mais bonus regulares seriam flamejantes. Para encurtar, Fogo777 Casino e uma pira de adrenalina para os fas de adrenalina ardente! Como extra o visual e uma explosao de chamas. criando uma experiencia de cassino incendiaria.
plataforma fogo777.com|
yourtrustedguideforlife – Typography feels warm, spacing gives good breathing room.
Estou completamente encantado com BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura cheia de emocao. As opcoes sao amplas como um campo de jogo, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, com suporte rapido e preciso. Os saques sao rapidos como um drible, as vezes bonus mais variados seriam um golaco. No geral, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para jogadores em busca de emocao ! Vale destacar a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Muito atrativo os pagamentos seguros em cripto, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Clicar para ver|
Sou totalmente viciado em PlayPIX Casino, e uma plataforma que transborda vitalidade. O catalogo e exuberante e diversificado, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. O bonus de boas-vindas e cativante. O acompanhamento e impecavel, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, as vezes bonus mais variados seriam incriveis. No fim, PlayPIX Casino e essencial para jogadores para fas de cassino online ! Tambem o site e rapido e cativante, adiciona um toque de conforto. Muito atrativo os torneios regulares para competicao, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Ver a pГЎgina|
A vibrant platformer guiding a panda through exciting puzzles and treasures. Fun and family-friendly: cute Panda games to play
фитнес клуб фитнес клуб с бассейном
TurnIdeasIntoAction – I appreciate how they encourage doing rather than just dreaming.
EverythingStartsWithYou – Great source for mindset shifts, gratitude, and forward momentum.
кафета торрент Фильмы 2023 скачать торрент Переживите заново эмоции от просмотра лучших фильмов 2023 года! На нашем сайте вы найдете широкий выбор кинокартин, которые покорили сердца зрителей в прошлом году. Мы предлагаем скачать фильмы 2023 торрент в высоком качестве, чтобы вы могли наслаждаться просмотром любимых фильмов в отличном качестве. У нас вы найдете фильмы различных жанров: от захватывающих экшенов и фантастических саг до трогательных мелодрам и комедийных историй. Наша коллекция постоянно пополняется, поэтому вы всегда сможете найти что-то интересное для себя. Благодаря удобной системе поиска и фильтрации вы легко сможете найти нужный фильм по названию, жанру, году выпуска, рейтингу и другим критериям. Скачивайте фильмы 2023 торрент быстро и безопасно с нашего сайта! Мы гарантируем высокое качество файлов и отсутствие вирусов. Наслаждайтесь просмотром лучших фильмов 2023 года в любое время и в любом месте!
LearnShareAndGrow – I’m excited to see the positive changes they are driving.
LearnSomethingAwesome – I keep discovering awesome facts and ideas I never knew before.
FindTheBestIdeas – The writing feels personal, like someone sharing honest advice and insights.
https://www.noosbox.com/how-to-buy-a-money-earn-on-a-shoestring-budget/
TheArtOfLivingWell – I appreciate the balance between motivation and gentle encouragement throughout.
FindAnswersAndIdeas – The topics are fresh and always get me curious to explore more.
YourDigitalDestination – It feels professional and welcoming at the same time.
FindNewWaysToGrow – I found this site just when I needed a fresh perspective today.
GetConnectedWithPeople – I’ve already met interesting people through this site, very cool.
UnlockYourPotentialToday – Their advice feels genuine, not just slogans—really appreciate that.
DiscoverWorldOfIdeas – Content is inspiring, makes me want to explore new creative paths daily.
FindSolutionsForLife – The layout’s clean, reading is smooth, no unnecessary clutter.
ConnectDiscoverAndGrow – This is such a friendly space, made me feel welcome right away.
markmackenzieforcongress – The posts here really help me stay informed about local concerns.
madeleinemtbc – I appreciate how inviting and clear the message is
FindInspirationEverywhere – The visuals paired with words really enhance the feeling and message.
YourGuideForSuccess – Definitely a resource I’ll keep coming back to when I need guidance.
DiscoverUsefulTipsDaily – The advice here is simple but surprisingly effective in practice.
StartChangingYourLife – Every article feels like a small push forward for me.
DiscoverNewOpportunities – It’s inspiring to see how they empower local communities.
BuildYourDreamFuture – There’s something uplifting about reading here after a rough day.
https://bs2site.gdn
заказать расклад таро Карьерный расклад таро Карьерный расклад таро – это специализированный расклад карт Таро, предназначенный для анализа карьерной ситуации и прогнозирования карьерных перспектив. Он помогает понять, какие возможности существуют для профессионального роста, какие риски следует учитывать при смене работы и как достичь успеха в карьере. Карьерный расклад таро может ответить на такие вопросы, как: Какова текущая карьерная ситуация? Какие возможности существуют для профессионального роста? Подходящая ли текущая работа? Какие риски следует учитывать при смене работы? Как достичь успеха в карьере? Какие навыки необходимо развивать для достижения карьерных целей? Карьерный расклад таро помогает увидеть карьерную ситуацию с другой стороны, понять скрытые факторы и принять взвешенные решения, направленные на достижение карьерного успеха.
сайт фитнес клуба фитнес клуб москва цены
LearnAndImproveEveryday – I really like the mix of theory and practical examples given here.
BeCreativeEveryday – Love the creative ideas here, they really spark inspiration daily.
скачать фильмы торрент Сериалы 2023 скачать торрент Переживите заново эмоции от просмотра лучших сериалов 2023 года! На нашем сайте вы найдете широкий выбор сериалов, которые покорили сердца зрителей в прошлом году. Мы предлагаем скачать сериалы 2023 торрент в высоком качестве, чтобы вы могли наслаждаться просмотром любимых сериалов в отличном качестве. У нас вы найдете сериалы различных жанров: от захватывающих детективных историй и фантастических саг до комедийных ситкомов и мелодраматических драм. Наша коллекция постоянно пополняется, поэтому вы всегда сможете найти что-то интересное для себя. Благодаря удобной системе поиска и фильтрации вы легко сможете найти нужный сериал по названию, жанру, году выпуска, рейтингу и другим критериям. Скачивайте сериалы 2023 торрент быстро и безопасно с нашего сайта! Мы гарантируем высокое качество файлов и отсутствие вирусов. Наслаждайтесь просмотром лучших сериалов 2023 года в любое время и в любом месте!
StayMotivatedAndFocused – The motivational tips are concise and really hit home for me.
Автобус стоимость заказа https://povozkin.ru
https://bs2site2.cc
натяжные потолки в нижнем новгороде stretch-ceilings-nizhniy-novgorod.ru .
makeprogressdaily – Always look forward to the new posts, they keep me on track.
makethemostoflife – The visuals and text work well together, nicely balanced
blsp at Заинтересован, что будоражит тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это эталон анонимности, оперативности и уверенности. Добро пожаловать на bs2best.at — место, где открывают то, о чём принято умалчивать. Здесь ты получишь доступ к запретному плоду. Только для избранных. Без улик. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти возможность стать первопроходцем — bs2best.at уже готов раскрыть свои секреты. Хватит ли тебе смелости взглянуть правде в лицо?
inspireandgrowtogether – I shared this with a friend, they’ll love it too.
findyourwayforward – I’ll be visiting again when I need direction or clarity
findthebestcontent – Shares just what I need, no fluff, very efficient content
licsupport – The design and content align well, feels trustworthy
discoverlearnandshare – Found something new I hadn’t seen elsewhere — neat find
growyourpresenceonline – I learned something I can use right away, appreciate it
discovertrendingideas – Good balance of depth and readability in posts
connectwithbrilliantminds – Very refreshing to see encouragement paired with clever ideas
learnandearndaily – It feels like someone wants to see readers succeed
everythingaboutmarketing – A must-visit site for staying updated on marketing best practices.
keepgrowingwithus – The tone is reassuring and helpful, good job
discoverhiddenpotential – The layout is user-friendly, making it easy to navigate and find resources.
discoveryourpassion – I feel more aligned with my purpose after visiting.
Лазерные станки https://raymark.ru для резки металла в Москве. 20 лет на рынке, выгодная цена, скидка 5% при заявке с сайта + обучение
learnexploreandshine – It motivates me to learn and share more often
HOME CLIMAT https://homeclimat36.ru кондиционеры и сплит системы в Воронеже. Скидка на монтаж от 3000 рублей! При покупке сплит-системы.
togetherwecreateimpact – I like how the message is hopeful without being overly idealistic
yourgatewaytosuccess – I was able to find resources fast, very smooth navigation
findyourinspirationhere – Already shared this with a friend who loves motivation
findyourwayforward – I’m looking forward to exploring more content here.
connectandgrowonline – This platform made it so easy to grow my business.
jointhenextbigthing – The design is sleek, navigation is simple, very user-friendly.
findyourinnerdrive – I shared this with a friend; they found it helpful too.
buildyourdigitalfuture – The content here is uplifting and practical, perfect for personal growth.
https://1-bs2best.lat
عزیزان، وبسایتهای قمار تهدیدکننده و
دروغین هستند. من به دلیل کنجکاوی فعال
گردیدم و در مدت کوتاه هفته بیشمار درآمدام را هدر دادم.
نه تنها مالی، همچنین روابط مرا نابود گردید.
وابستگی نسبت به این فعالیتها مثل زنجیری است که شما را در ویرانی میبرد.
به هیچ عنوان تست نکنید!
buildyourownlegacy – I’d recommend this to friends working on self-growth
bs2best at Заинтересован, что будоражит тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это эталон анонимности, оперативности и уверенности. Добро пожаловать на bs2best.at — место, где открывают то, о чём принято умалчивать. Здесь ты получишь доступ к запретному плоду. Только для избранных. Без улик. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти возможность стать первопроходцем — bs2best.at уже готов раскрыть свои секреты. Хватит ли тебе смелости взглянуть правде в лицо?
findsolutionsfast – Easy to browse, didn’t struggle to find what I needed
نکته فوری به سایتهای بازیهای شرطی.
چنین سایتها ساخته میشوند تا افراد را وابسته شوند و سرمایهتان را غارت بکنند.
من در سبب آگهیها دلربا فعال کردم و عاقبت نابودی گردید.
وابستگی روانی همچنین زیان پولدار دو جانبه میباشد.
به هیچ وجه امتحان نخواهید!
startyourdreamproject – I’ll bookmark this as a go-to resource when I start something
buildyourdreambrand – The layout is clean and inspiring rather than overwhelming
Нужна недвижимость? купить недвижимость Черногория лучшие объекты для жизни и инвестиций. Виллы, квартиры и дома у моря. Помощь в подборе, оформлении и сопровождении сделки на всех этапах.
Аутстаффинг персонала https://skillstaff2.ru для бизнеса: легальное оформление сотрудников, снижение налоговой нагрузки и оптимизация расходов. Работаем с компаниями любого масштаба и отрасли.
Do you have a spam issue on this blog; I also am a blogger, and I was wondering your situation; many of
us have created some nice procedures and we are looking to exchange methods with others, be sure to
shoot me an e-mail if interested.
Іt’s perfect tіme to make some plans fοr thе future ɑnd іt is
time to bе һappy. I’ve read tһis post and if І сould I wіsh to suggest yօu somе interesting thingѕ oг tips.
Perhapѕ yoᥙ couⅼⅾ ѡrite next articles referring tο this article.
Ι ᴡant to read more thіngs about it!
everythingyouneedtoday – Good balance between visuals and text, nothing overwhelms
антицеллюлитный массаж SMAS лифтинг SMAS лифтинг – это хирургическая операция по подтяжке лица, направленная на укрепление и подтяжку не только кожи, но и более глубоких слоев тканей, включая SMAS (Superficial Muscular Aponeurotic System) – мышечно-апоневротический слой. SMAS лифтинг обеспечивает более выраженный и долгосрочный эффект омоложения лица.
Curto demais a energia de BR4Bet Casino, e uma onda de diversao que cintila como um farol. Os jogos formam um clarao de entretenimento. incluindo mesas com charme iluminado. Os agentes voam como claroes. garantindo suporte direto e sem escuridao. Os pagamentos sao lisos como uma chama. de vez em quando queria mais promocoes que brilham como farois. No fim das contas, BR4Bet Casino e um clarao de emocoes para os cacadores de vitorias reluzentes! Alem disso a navegacao e facil como um facho de luz. criando uma experiencia de cassino reluzente.
480|
Acho simplesmente brabissimo MegaPosta Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e pura dinamite. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo insano, com slots de cassino unicos e contagiantes. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um raio. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma tempestade, mesmo assim mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Resumindo, MegaPosta Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os aventureiros do cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia explosiva, aumenta a imersao no cassino a mil.
bet megaposta|
Acho simplesmente insano OshCasino, da uma energia de cassino que e um terremoto. Tem uma enxurrada de jogos de cassino irados, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O atendimento ao cliente do cassino e uma faisca de eficiencia, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como uma erupcao, de vez em quando queria mais promocoes de cassino que incendeiam. No fim das contas, OshCasino garante uma diversao de cassino que e um vulcao para os aventureiros do cassino! Alem disso a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia ardente, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como uma erupcao.
osh classic|
Ich kann nicht genug bekommen von NV Casino, es ist ein Abenteuer, das pulsiert wie ein Herzschlag. Die Vielfalt der Titel ist atemberaubend, mit Spielen, die perfekt fur Kryptos geeignet sind. Der Service ist rund um die Uhr verfugbar, immer bereit zu helfen. Die Gewinne kommen ohne Verzogerung, ab und zu zusatzliche Freispiele waren toll. Insgesamt, NV Casino garantiert Top-Unterhaltung fur Adrenalin-Junkies ! Zusatzlich die Site ist schnell und elegant, was jede Session noch spannender macht.
playnvcasino.de|
Sou viciado em BETesporte Casino, oferece um thrill esportivo unico. O catalogo e rico e diversificado, com sessoes ao vivo imersivas. Fortalece seu saldo inicial. O suporte ao cliente e de elite, sempre pronto para o jogo. Os pagamentos sao seguros e fluidos, no entanto ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. No geral, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Vale destacar o site e veloz e envolvente, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Outro destaque os pagamentos seguros em cripto, oferece recompensas continuas.
Ver os detalhes|
bs2best зеркало Интересуешься, что происходит в тёмных уголках сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название, это гарантия анонимности, высокой скорости и надежности. Переходи на bs2best.at — там ты найдёшь то, о чём другие умалчивают. Тебе откроется доступ к информации, которую скрывают от большинства. Только для тех, кто понимает. Без компрометирующих следов. Без уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти шанс узнать первым — bs2best.at уже готов открыть свои двери. Дерзнешь ли ты взглянуть правде в глаза?
bet bonus codes Bet bonus will enhance your betting experience with extra funds and more chances to win. Get matched deposits and risk-free bets with exclusive betting bonus codes. Don’t wait, claim yours today!
group chat
learnnewthingsdaily – Very encouraging tone, makes learning feel fun and doable.
shareyourvisiontoday – I’ve bookmarked it, will return often for guidance.
votethurm – I saw this link on social media, looks like a political page.
discovergreatideas – Inspired me to think outside the box for my startup.
inspireeverymoment – Thank you for sharing these little sparks of inspiration.
growtogetherwithus – Thanks for this space, it’s helping me stay committed to growth.
inspireeverymoment – Thank you for sharing these little sparks of inspiration.
startyourdigitaljourney – This site made it possible for me to go digital.
thefuturestartsnow – The writing is engaging and pushes me to act now.
theartofsuccess – Brilliant mix of mindset and practical steps to grow.
yourjourneytowin – I bookmarked it, will revisit when I need to refocus.
createimpactfulstories – The stories here push me to share more of my own experiences.
staycuriousandcreative – Really enjoy the visuals and how ideas unfold here.
Строительный портал https://v-stroit.ru всё о строительстве, ремонте и архитектуре. Полезные советы, технологии, материалы, новости отрасли и практические инструкции для мастеров и новичков.
findyourcreativeflow – The suggestions here are simple yet deeply impactful for creators.
yourpathofsuccess – Loved the recent post, made me rethink my strategy.
creativityneverends – So inspiring, every post gives me fresh energy and new perspectives.
маммография екатеринбург Денситометрия Денситометрия – это метод исследования плотности костной ткани, используемый для диагностики остеопороза. Денситометрия позволяет определить риск переломов костей и назначить необходимое лечение.
https://t.me/pikmaninfo What we do I lead a powerful team that is shaping the future of B2B Saas go-to-market strategies. My company Pikman.info helps high-growth B2B companies with Demand, Attribution & Analytics, and Revenue R&D by delivering a suite of proprietary research, revenue analytics tools, and GTM experimentation services. Pikman.info helps B2B SaaS companies create and capture demand through paid ads to drive a more qualified pipeline for your sales team. Growth at all costs is over, and sustainable growth is what your SaaS brand needs. That means optimizing for the lowest cost per opportunity, not the lowest cost per lead.
startcreatingimpact – Practical advice here motivates me to really take action daily.
Портал о строительстве https://pamel-stroy.ru и ремонте. Пошаговые инструкции, идеи, технологии, новости и советы экспертов. Всё, что нужно, чтобы строить и ремонтировать грамотно.
yourmomenttoshine – I visited just now and felt truly empowered by your messages.
Риэлторская контора https://daber27.ru покупка, продажа и аренда недвижимости. Помогаем оформить сделки безопасно и выгодно. Опытные риэлторы, консультации, сопровождение и проверка документов.
Купольные дома https://kupol-doma.ru под ключ — энергоэффективные, надёжные и современные. Проектирование, строительство и отделка. Уникальная архитектура, комфорт и долговечность в каждом доме.
stacoa.org – Looking forward to learning more from the content here.
myvetcoach.org – I bookmarked this — will definitely revisit for deeper resources.
filamericansforracialaction.com – Good to see WordPress used, content seems accessible and organized.
electlarryarata – The homepage is clean but I expected more content already.
thespeakeasybuffalo – I noticed “Nothing found” currently; hope content fills soon.
laetly.com – Couldn’t see much content, looking forward to updates.
growyourdigitalpresence – Fingers crossed, implementing their advice helped my traffic improve.
norigamihq – For now it’s mysterious, but the name is memorable.
summerstageinharlem.org – The venue at 125th St looks iconic and full of history.
pinellasehe.org – Very nice site, I found several useful insights just browsing.
formative-coffee.com – The blog section is lovely, full of interesting coffee culture reads.
rockyrose.org – The articles here are thoughtful, I read with interest.
hecimagine.com – The mission seems powerful — business + peace through education.
Ваша Недвижимость https://rbn-khv.ru сайт о покупке, продаже и аренде жилья. Разбираем сделки, налоги, ипотеку и инвестиции. Полезная информация для владельцев и покупателей недвижимости.
Информационный блог https://gidroekoproekt.ru для инженеров и проектировщиков. Всё об инженерных изысканиях, водохозяйственных объектах, гидротехническом строительстве и современных технологиях в отрасли.
mystylecorner – Checkout was simple and fast, appreciated that a lot.
https://t.me/pikmaninfo PR & Marketing Expertise: Data-Driven Marketing, Paid Search/SEM (Linkedin Ads, Facebook Ads, Google Ads, YouTube Ads, Yandex Ads, Bing Ads), Search Engine Optimization/SEO, Display, Retargeting, Social Media/SMM, Paid Media, Account Based Marketing/ABM, Digital Marketing/Strategy, Data Analytics, Customer Acquisition, Web Marketing, Business Development, Full Stack Marketing, Customer Journey, Content Marketing, A/B Split Testing, Budget Management, Conversational Marketing, Conversion Rate Optimization, Growth Marketing, Multi-Touch Attribution, Copywriting, Data Journalism, Content writing, Visual Storytelling, Brand Identity, Web Design UX/UI, Digital Media, Content Marketing, Demand Generation, Forecasting and Modeling.
creativevision – Each piece tells a unique story, sparking deep reflection.
successpartnersgroup – Honestly didn’t expect to like it this much, great vibes.
newseason – Love the product photography—details show nicely, feels trustworthy.
trendyfashioncorner – Browsing was smooth, found trendy pieces that match my style.
globalideasnetwork – The content here is inspiring, makes me want to explore more.
cryptotephra-clagr.com – I found references to a “Cryptotephra CLAGR” lab tied to UNLV.
ukrainianvictoryisthebestaward.com – Looks like the domain’s been reused or repurposed.
discovernewideas – The homepage grabbed me immediately, great first impression all around.
inspiredgrowthteam – Could browse for hours, site feels professional and motivating.
createimpact – Always nice to see clarity and quality together in one place.
luxurytrendstore – The seasonal collections are on point, perfect for updating my wardrobe.
visionaryleadersclub – The site gives confidence, feels polished yet accessible.
partnershippowerhouse – I really like how their about page gives insight without being overwhelming.
trendymodernwear – The website is user-friendly, easy to navigate and shop.
successpartnersgroup – Navigation feels smooth, pages load quickly, very user-friendly overall.
free bet promotions Online Betting Deals “Online betting deals” encompass the multiple promotional offers that bookies put out to grab fresh punters and hook current gamblers. Deals may allow punters to gain increased prices when wagering. Rewards and cashback programs may have the effect of reducing a gambler’s total losses. Before taking the online action, gamblers must always examine conditions. By selecting deals, punters can extend their action.
blsp at Готов узнать, что творится в глубинах тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это символ анонимности, скорости и безопасности, а не просто бренд. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не говорить. Тебе откроют все тайны, скрытые от посторонних глаз. Только для посвящённых. Никаких следов. Никаких полумер. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс быть впереди — bs2best.at ждёт тех, кто готов к новому. Осмелишься ли ты узнать истину?
digitaledge – I keep discovering interesting posts, design is consistent throughout.
alternative music
urbanwearzone – Hands down one of the most user-friendly fashion shops I saw.
futuremindscollective – Excited to support a brand that invests in the future of education.
Ich bin total begeistert von Lowen Play Casino, es bietet ein Casino-Abenteuer, das wie ein Urwald leuchtet. Der Katalog des Casinos ist ein Dschungel voller Nervenkitzel, mit modernen Casino-Slots, die einen in ihren Bann ziehen. Der Casino-Service ist zuverlassig und machtig, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Lowenangriff. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, manchmal mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren ein Volltreffer. Am Ende ist Lowen Play Casino ein Online-Casino, das die Savanne beherrscht fur Spieler, die auf wilde Casino-Kicks stehen! Zusatzlich die Casino-Seite ist ein grafisches Meisterwerk, einen Hauch von Abenteuer ins Casino bringt.
löwen play konstanz|
Acho simplesmente insano JabiBet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e uma mare alta. As opcoes de jogo no cassino sao ricas e eletrizantes, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. Os agentes do cassino sao rapidos como uma onda, dando solucoes na hora e com precisao. Os saques no cassino sao velozes como um redemoinho, as vezes mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. Na real, JabiBet Casino vale demais explorar esse cassino para os amantes de cassinos online! De bonus o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais alucinante.
jabibet casino|
Estou pirando com PagolBet Casino, da uma energia de cassino que e um raio. Os titulos do cassino sao um espetaculo eletrizante, com jogos de cassino perfeitos pra criptomoedas. O suporte do cassino ta sempre na ativa 24/7, respondendo mais rapido que um raio. O processo do cassino e limpo e sem turbulencia, porem mais bonus regulares no cassino seria top. Na real, PagolBet Casino oferece uma experiencia de cassino que e puro choque para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! E mais a plataforma do cassino detona com um visual que e puro trovao, faz voce querer voltar pro cassino como um raio.
pagolbet app|
Ich bin beeindruckt von SpinBetter Casino, es erzeugt eine Spielenergie, die fesselt. Das Angebot an Spielen ist phanomenal, mit immersiven Live-Sessions. Der Kundenservice ist ausgezeichnet, garantiert top Hilfe. Die Gewinne kommen prompt, gelegentlich mehr Rewards waren ein Plus. In Kurze, SpinBetter Casino ist eine Plattform, die uberzeugt fur Krypto-Enthusiasten ! Zusatzlich die Plattform ist visuell ein Hit, was jede Session noch besser macht. Ein weiterer Vorteil die Community-Events, die den Spa? verlangern.
spinbettercasino.de|
Ich kann nicht genug bekommen von NV Casino, es bietet eine Reise voller Spannung. Es wartet eine Fulle an spannenden Spielen, mit dynamischen Live-Sessions. Die Mitarbeiter reagieren blitzschnell, bietet klare Antworten. Die Zahlungen sind sicher und flussig, obwohl regelma?igere Promos waren super. Zusammengefasst, NV Casino ist ein Muss fur Gamer fur Fans von Online-Wetten ! Hinzu das Design ist modern und ansprechend, macht die Erfahrung flussiger.
playnvcasino.de|
What’s up, constantly i used to check weblog posts here in the early hours in the break of day, as i love to gain knowledge of more and more.
официальный сайт leebet
discovernewpath – Mission statement speaks well, feels like they know their purpose.
Tenho uma paixao vibrante por BETesporte Casino, proporciona uma aventura eletrizante. As opcoes sao amplas como um campo de futebol, oferecendo jogos de mesa envolventes. O bonus de boas-vindas e empolgante. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, sempre pronto para entrar em campo. Os saques sao rapidos como um contra-ataque, no entanto ofertas mais generosas dariam um toque especial. Para finalizar, BETesporte Casino vale uma aposta certa para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Acrescentando que o design e moderno e vibrante, facilita uma imersao total. Muito atrativo os torneios regulares para rivalidade, oferece recompensas continuas.
Ver a pГЎgina|
Currently it appears like Movable Type is the top blogging platform out there right now. (from what I’ve read) Is that what you are using on your blog?
зеркало банда казино
bs2best at Неужели ты до сих пор не знаешь, что переворачивает мир даркнета? Blacksprut – это не просто название. Это новая эра анонимности, мгновенной скорости и железобетонной безопасности в сети. Загляни на bs2best.at – туда, где обсуждают то, о чём остальные предпочитают молчать в тряпочку. Тебе откроется доступ к информации, тщательно оберегаемой от посторонних глаз. Только для тех, кто понимает правила игры. Никаких следов, никаких компромиссов, только абсолютная конфиденциальность – это Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс стать первооткрывателем – bs2best.at уже распахнул свои двери для тебя. Хватит ли у тебя смелости взглянуть правде прямо в лицо?
findyourfuture – Clean visuals and easy navigation make browsing enjoyable.
trustconnectionnetwork – Secure payment options provide peace of mind during transactions.
uniquefashionstyle – The clean layout enhances the overall shopping journey.
video broadcast
nextvision – If this is a promotional page, they need stronger details for trust.
trustedbusinesslink – Love the visual coherence, branding feels strong and consistent.
futureopportunitynetwork – The content is engaging and relevant, keeping me informed.
growstrongteam – Love how clean and bold the design feels, very inspiring.
futurevisiongroup – The site feels futuristic but grounded, very nice aesthetic.
learnsharegrow – I’ll be checking back for new content or updates soon.
happylifestylehub – I find fresh ideas every time, really inspiring place.
growthpoint – Professional branding, good use of space and design elements.
futureopportunitynetwork – I found what I was looking for quickly, no confusion.
buildbrand – The strategies outlined are applicable to businesses of all sizes.
bs market Неужели ты до сих пор не знаешь, что переворачивает мир даркнета? Blacksprut – это не просто название. Это новая эра анонимности, мгновенной скорости и железобетонной безопасности в сети. Загляни на bs2best.at – туда, где обсуждают то, о чём остальные предпочитают молчать в тряпочку. Тебе откроется доступ к информации, тщательно оберегаемой от посторонних глаз. Только для тех, кто понимает правила игры. Никаких следов, никаких компромиссов, только абсолютная конфиденциальность – это Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс стать первооткрывателем – bs2best.at уже распахнул свои двери для тебя. Хватит ли у тебя смелости взглянуть правде прямо в лицо?
https://t.me/pikmaninfo PR & Marketing Expertise: Data-Driven Marketing, Paid Search/SEM (Linkedin Ads, Facebook Ads, Google Ads, YouTube Ads, Yandex Ads, Bing Ads), Search Engine Optimization/SEO, Display, Retargeting, Social Media/SMM, Paid Media, Account Based Marketing/ABM, Digital Marketing/Strategy, Data Analytics, Customer Acquisition, Web Marketing, Business Development, Full Stack Marketing, Customer Journey, Content Marketing, A/B Split Testing, Budget Management, Conversational Marketing, Conversion Rate Optimization, Growth Marketing, Multi-Touch Attribution, Copywriting, Data Journalism, Content writing, Visual Storytelling, Brand Identity, Web Design UX/UI, Digital Media, Content Marketing, Demand Generation, Forecasting and Modeling.
Деревянные лестницы https://rosslestnica.ru под заказ в любом стиле. Прямые, винтовые, маршевые конструкции из массива. Замеры, 3D-проект, доставка и установка. Гарантия качества и точности исполнения.
Лестницы в Москве https://лестницы-в-москве.рф продажа и изготовление под заказ. Прямые, винтовые, модульные и чердачные конструкции. Качество, гарантия и монтаж по всем стандартам.
unitedbygoal – Lots of motivation in their messaging, felt genuinely inspiring.
teamfuture – Friendly tone, helpful advice, everything flows well together.
businessgrowthhub – I appreciate the clarity, content feels practical and no fluff.
trustandunity – I enjoy how every message focuses on integrity and togetherness.
digitalinnovationzone – Good mix of tech and strategy, very relevant to what I need.
futuregoalsnetwork – I enjoy reading, content is inspiring without being overwhelming.
successbridge – I like the balance between inspiration and actionable steps here.
https://pdchoa.com/hello-world-2/
getthedeal – Deals are legit, purchased multiple items without any issues yesterday.
leadersunitedgroup – Feels like a community, not just a site, very welcoming tone.
connectinnovationhub – This place feels like learning meets creativity, very engaging tone.
winmore – I like the energy here, feels ambitious and motivating.
futuregoalsnetwork – I’m impressed with the consistency and thoughtful approach here.
findsomethingnew – Always find something that captures my interest here.
leadersunitedgroup – I like the leadership vibe here, feels motivating and real.
exploreideasworld – I find inspiration in almost every post, feels lively.
globalpartnershipteam – This seems like a place built on trust, I feel comfortable browsing.
successjourneyclub – I like how encouraging everything feels here, really uplifting vibe.
discovervalue – I like how much value things here really deliver, no fluff.
discoverdaily – I’ve bookmarked several posts, they keep surprising me.
trustconnectionnetwork – The tone feels warm and the message feels authentic, well done.
connectinnovationhub – I love the collaborative spirit here, feels energetic and alive.
growtogetheralliance – Visit after visit I feel more inspired, great energy overall.
brightdeal – The design is crisp and inviting — makes me want to explore more.
innovateandbuild – The design’s clean and modern, makes exploring fun and easy.
buildtogether – Excited to see more posts, this looks like a growing platform.
growthnetwork – I’ve bookmarked this site, seems rich with useful insights.
modernhomeessentials – Nice balance of style and function, products seem thoughtfully chosen.
businessgrowthhub – Clean design makes learning easy, I’m enjoying exploring.
fan meet
boldpartner – I found useful ideas here for collaborating better, thanks.
nextgeninnovation – I really like the forward-thinking feel, very inspiring design.
Adoro o brilho de Richville Casino, e um cassino online que reluz como um palacio dourado. A gama do cassino e um verdadeiro palacio de delicias, com slots de cassino tematicos de luxo. O servico do cassino e confiavel e majestoso, garantindo suporte de cassino direto e sem falhas. Os ganhos do cassino chegam com a velocidade de um jato particular, as vezes queria mais promocoes de cassino que brilhem como diamantes. Resumindo, Richville Casino promete uma diversao de cassino reluzente para os que buscam a adrenalina luxuosa do cassino! Vale dizer tambem a interface do cassino e fluida e brilha como um salao de baile, eleva a imersao no cassino ao apice.
offices in richville corporate tower|
brightmind – I really like how calm and thoughtful everything is here, very soothing.
Estou pirando total com JabiBet Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo que e puro tsunami. A gama do cassino e simplesmente um maremoto, com slots de cassino unicos e empolgantes. O servico do cassino e confiavel e brabo, respondendo mais rapido que um maremoto. Os ganhos do cassino chegam voando como uma onda, mas mais recompensas no cassino seriam um diferencial brabo. No fim das contas, JabiBet Casino garante uma diversao de cassino que e uma mare cheia para quem curte apostar com estilo no cassino! De lambuja a interface do cassino e fluida e cheia de energia oceanica, o que deixa cada sessao de cassino ainda mais alucinante.
jabibet casino bonus code|
Galera, resolvi contar como foi no 4PlayBet Casino porque foi muito alem do que imaginei. A variedade de jogos e muito completa: slots modernos, todos sem travar. O suporte foi amigavel, responderam em minutos pelo chat, algo que passa seguranca. Fiz saque em Ethereum e o dinheiro entrou sem enrolacao, ponto fortissimo. Se tivesse que criticar, diria que senti falta de ofertas recorrentes, mas isso nao estraga a experiencia. Enfim, o 4PlayBet Casino e completo. Com certeza vou continuar jogando.
4play strip club|
Sou viciado em PlayPIX Casino, e uma plataforma que pulsa com energia festiva. Ha uma explosao de jogos emocionantes, incluindo apostas esportivas vibrantes. O bonus de boas-vindas e vibrante. A assistencia e eficiente e cortes, garantindo um atendimento de qualidade. As transacoes sao confiaveis, de vez em quando mais promocoes regulares seriam otimas. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para amantes de emocoes intensas ! Alem disso a plataforma e visualmente espetacular, instiga a prolongar a experiencia. Um diferencial importante os eventos comunitarios envolventes, oferece recompensas continuas.
http://www.playpixcasino.pro|
Estou completamente empolgado com BETesporte Casino, sinto uma energia de estadio. As opcoes sao vastas como um campeonato, com slots modernos e tematicos. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. Os agentes respondem com velocidade, sempre pronto para o jogo. As transacoes sao confiaveis, embora bonus mais variados seriam um gol. No geral, BETesporte Casino oferece uma experiencia inesquecivel para amantes de apostas esportivas ! Vale destacar o site e veloz e envolvente, aumenta o prazer de apostar. Muito atrativo os eventos comunitarios envolventes, fortalece o senso de comunidade.
Encontrar os detalhes|
creativeworldstudio – The designs here are so imaginative, love every creative detail.
Smart approach is to buy fifa coins during weekday lulls when both coin prices and player markets stabilize naturally. Real active sellers with fast turnaround and non drop guarantees help capitalize on optimal purchasing windows for maximum value efficiency.
перепланировка согласование https://soglasovanie-pereplanirovki-kvartiry3.ru .
проект на перепланировку квартиры цена https://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry17.ru .
согласование согласование .
bs2best at Готов ли ты раскрыть тайны, окутывающие тёмную сеть? Blacksprut — это не просто бренд, это гарантия конфиденциальности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной безопасности. Посети bs2best.at и узнай то, о чём остальные предпочитают не упоминать. Тебе откроются все тайны, тщательно скрываемые от посторонних глаз. Только для избранных, обладающих особым знанием. Не оставляя следов. Без каких-либо компромиссов. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти уникальный шанс оказаться в авангарде — bs2best.at уже ждёт тех, кто стремится к открытиям. Сможешь ли ты осмелиться познать истинное положение вещей?
businessgrowthhub – I find fresh business ideas each time I explore this.
smartpartnership.bond – Their values seem solid and their goals are clearly stated.
inspiredmind.shop – The visuals are strong and navigation is smooth, well done.
smartdesigncorner.shop – Already showing this to friends looking for design inspiration.
creativegiftzone.shop – I love the variety — perfect for picking unique presents.
smartdesigncorner.space – Found some great ideas here for my next design project.
inspiredideas.shop – I just visited, such a creative selection and easy browsing.
trendfinder.bond – My go-to place whenever I want to spot new trends fast.
partnershippowerhouse.shop – Content looks strong and compelling, makes me want to join forces.
buildbrand.online – Really strong branding ideas here, definitely inspiring and useful.
trustinyou.bond – I feel more motivated just browsing this site — nice energy.
globalunity.bond – Design and visuals feel professional and hopeful.
shopwithpurpose.shop – I bookmarked several things — love the mindful style here.
creativityuniverse.shop – Unique pieces everywhere, feels like a place for creative souls.
https://plisio.net/ar/blog/fantom-ftm-is-this-fast-blockchain-the-next-ethereum
dailyvaluehub.shop – Great variety, competitive prices, and quality looks promising too.
Курсы ЕГЭ обществознание https://courses-ege.ru
brightfuturegroup.bond – Great layout, easy to navigate, everything feels intentional.
inspiredgrowthteam.shop – Found something that really resonated with me, good find!
visionaryleadersclub.bond – Inspiring stories and tools — exactly what I’ve been looking for.
buildlastingtrust.bond – Definitely sharing this with folks who value integrity in partnerships.
startsomethingnew.shop – Great design, smooth navigation — makes exploring a joy.
findnewtrend.shop – Love the vibe here—very up-to-date and stylish items.
smartstylehub.shop – I bookmarked several items, will come back for them.
trustedbusinesslink.shop – Their about section is clear; good to see transparency.
trustandunity.shop – Found several items I’d consider; good variety too.
globalpartnershipteam.bond – The site seems well structured, easy to understand partnerships.
modernchoice.store – Good images and solid layout — gives trust in what’s offered.
visionaryconnect.bond – Definitely sharing this — others need to see this vision too.
buildlastingties.bond – I appreciate how honest and sincere the content feels.
bs2web at Ты еще не в курсе, что порождает бурю в темных водах сети? Blacksprut – это не просто символ. Это квинтэссенция анонимности, молниеносной скорости и абсолютной уверенности в каждом действии. Приглашаем на bs2best.at – туда, где шепчут о том, о чем другие предпочитают хранить гробовое молчание. Тебе откроются двери в мир, скрытый от любопытных глаз, доступный лишь избранным, тем, кто понимает истинную цену информации. Ни единой зацепки. Никаких отступлений. Только безупречный Blacksprut, гарант твоей конфиденциальности. Не упусти свой шанс стать первопроходцем – bs2best.at уже готов раскрыть свои тайны. Достаточно ли ты смел, чтобы заглянуть в бездну правды?
https://plisio.net/pl/blog/shakira-net-worth
growtogetheralliance.shop – The vibe is optimistic and genuine, which I dig.
streaming event
investsmarttoday – Great content for beginners and experienced investors, highly recommend this.
successjourneyclub.shop – The tone feels authentic, makes me feel like they really want people to grow.
brightmarketplace – Smooth browsing and secure payment options, very trustworthy site.
smartbuytoday – Impressed with the packaging and timely delivery, will shop again.
justvotenoon2 – Really practical advice, I’ll definitely try these suggestions soon.
classytrendstore – Trendy styles at great prices, found exactly what I needed.
bestdealcorner – Helpful product descriptions and reviews, made decision-making easier today.
everydayvaluefinds.shop – Clean design and easy browsing make shopping here fun.
modernvisionlab.shop – Prices seem reasonable for what’s shown, good balance.
dailyprofitupdate – Found some great deals; checkout process was quick and secure.
modernvaluecorner – Found some great deals; checkout process was quick and secure.
stylemebetter – Love the clean design; makes shopping a pleasant experience.
buildlastingtrust.shop – Sharing this with people who appreciate transparent, meaningful work.
Adoro a correnteza de Brazino Casino, explode com uma vibe aquatica eletrizante. A selecao de titulos e uma correnteza de emocoes. com caca-niqueis que reluzem como perolas. O atendimento esta sempre ativo 24/7. com ajuda que ilumina como uma perola. Os ganhos chegam rapido como uma corrente. entretanto mais bonus seriam um diferencial oceanico. Em resumo, Brazino Casino e o point perfeito pros fas de cassino para os exploradores de jogos online! Vale dizer a plataforma reluz com um visual oceanico. amplificando o jogo com vibracao aquatica.
jogo brazino777 paga mesmo|
findyourlook.shop – Already bookmarked several pieces, thinking about ordering soon.
nextgenproject.shop – Layout is promising, assuming content matches the vision.
Sou louco pelo batuque de SambaSlots Casino, tem uma vibe de jogo tao vibrante quanto um bloco de rua. A selecao de titulos do cassino e um desfile de cores, com caca-niqueis de cassino modernos e contagiantes. A equipe do cassino entrega um atendimento que e puro carnaval, com uma ajuda que e puro axe. As transacoes do cassino sao simples como um passo de samba, porem mais giros gratis no cassino seria uma loucura. Em resumo, SambaSlots Casino e um cassino online que e uma festa de diversao para quem curte apostar com gingado no cassino! E mais o site do cassino e uma obra-prima de estilo carioca, torna a experiencia de cassino uma festa inesquecivel.
code bonus la sambaslots casino 2020|
Ich liebe den Wahnsinn von JackpotPiraten Casino, es ist ein Online-Casino, das wie eine Welle kracht. Die Auswahl im Casino ist ein echter Jackpot, mit Casino-Spielen, die fur Kryptowahrungen optimiert sind. Die Casino-Mitarbeiter sind schnell wie ein Piratenschiff, antwortet blitzschnell wie ein Sabelhieb. Casino-Zahlungen sind sicher und reibungslos, dennoch mehr regelma?ige Casino-Boni waren der Hammer. Alles in allem ist JackpotPiraten Casino ein Casino, das man nicht verpassen darf fur die, die mit Stil im Casino wetten! Ubrigens das Casino-Design ist ein optischer Volltreffer, den Spielspa? im Casino auf Hochtouren bringt.
promo code jackpotpiraten|
trendhunterplace – The layout is smooth and easy to explore, very nice.
modernwoodcases – These cases make fantastic gifts; always a hit with friends.
bs2best зеркало В курсе ли ты, что сотрясает самые глубины тёмной сети? Blacksprut — это не просто название. Это новый уровень в обеспечении анонимности, оперативности и безопасности сделок. Посети bs2best.at — там тебе откроются двери в мир, о котором другие предпочитают умалчивать. Получи доступ к информации, которую тщательно скрывают от общего внимания. Только для тех, кто понимает и разбирается. Без возможности обнаружения. Без каких-либо уступок. Только Blacksprut. Не упусти свой шанс стать одним из первых — bs2best.at уже готов принять тебя в свои ряды. Готов ли ты к тому, что узнаешь?
yourtradingmentor – Practical trading tips that save a lot of time and effort today.
J’apprecie enormement 7BitCasino, ca procure une plongee dans un univers palpitant. Les options de jeu sont riches et diversifiees, comprenant plus de 5 000 jeux, dont 4 000 adaptes aux cryptomonnaies. Le service d’assistance est de premier ordre, avec un suivi de qualite. Les paiements sont fluides et securises, occasionnellement davantage de recompenses seraient appreciees, afin de maximiser l’experience. En fin de compte, 7BitCasino offre une experience de jeu securisee et equitable pour les passionnes de jeux numeriques ! Par ailleurs le site est concu avec style et modernite, renforce l’immersion totale.
7bitcasino usa|
purebeautyoutlet – I found exactly what I wanted quickly, excellent search feature.
trendinggiftcorner – Easy to browse and find unique gifts, highly recommend this.
smarttradingmentor – Helpful insights and strategies, learned a lot just browsing the tutorials.
musionet – Great tips and resources, highly recommend to everyone visiting.
Fiquei impressionado com PlayPIX Casino, transmite uma energia vibrante. O catalogo e rico e multifacetado, suportando jogos compativeis com criptomoedas. 100% ate €500 + rodadas gratis. A assistencia e eficiente e amigavel, garantindo atendimento de alto nivel. As transacoes sao confiaveis, de vez em quando recompensas extras seriam eletrizantes. Em sintese, PlayPIX Casino vale uma visita epica para amantes de emocoes fortes ! Alem disso a interface e fluida e estilosa, adiciona um toque de conforto. Notavel tambem os pagamentos seguros em cripto, assegura transacoes confiaveis.
Ir para a web|
newhorizonsnetwork.bond – Navigation is smooth; content seems thoughtful so far.
Amo a energia de BETesporte Casino, oferece um prazer esportivo intenso. O catalogo e vibrante e diversificado, com sessoes ao vivo cheias de energia. Eleva a experiencia de jogo. Os agentes respondem com rapidez, oferecendo respostas claras. Os ganhos chegam sem atraso, embora mais apostas gratis seriam incriveis. Em sintese, BETesporte Casino garante diversao constante para entusiastas de jogos modernos ! Tambem a navegacao e intuitiva e rapida, tornando cada sessao mais competitiva. Um diferencial importante os torneios regulares para rivalidade, que impulsiona o engajamento.
Ir para o site|
protraderacademy – Very helpful guides for beginners, learned a lot in minutes today.
fastgrowthsignal – Overall pleasant experience, will revisit for future purchases very soon.
tradingmasterclass – Helpful tips for both beginners and advanced traders, excellent platform.
brightfuturegroup.shop – I like how it gives off a positive, forward-thinking vibe right away.
strongpartnershipnetwork – Easy to follow tips and strategies, really improved my approach.
ultimateprofitplan – Clear and concise, perfect for entrepreneurs looking to grow efficiently.